In natural gas distribution, the choice of materials is crucial for a pipeline system’s safety, efficiency, and durability. Polyethylene (PE) pipes for gas have become a popular option due to their unique properties and advantages over conventional ones. This paper will take an in-depth look at PE gas pipes, discussing their features, benefits, installation procedures, and regulatory requirements. By understanding the basics of PE gas piping, readers can comprehend the significance of this particular pipe in modern natural gas infrastructures with its broad-based acceptance. Whether you are a professional in the sector or just somebody who wants to know how gases are distributed, this manual provides all you need to understand PE gas pipes, including their significant roles.
What is PE Gas Pipe, and How is it Used?

Image source: https://www.pipelife.co.uk/
Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pipe is a flexible and durable plastic piping system designed specifically for natural gas distribution. They are made from high-density polyethylene, making them resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and impact and appropriate for various environmental conditions. Because they are lightweight and easy to handle compared to other types of underground installations, PE gas pipes are usually used in such constructions, reducing installation costs incurred. These types of pipelines find typical applications in residential as well as commercial and industrial areas where they convey natural gases safely from sources serving end-users. Moreover, there is a reduced risk of leakage since these pipes do not have joints, increasing safety during gas delivery services.
Understanding Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pipes
In my investigation of polyethylene (PE) gas pipes, I discovered that they are known for being extremely flexible and robust, making them suitable for a wide range of uses in gas distribution. One thing that stood out is that these pipes do not rust easily and can survive many environmental conditions, ensuring their durability, mainly when used underground. Moreover, PE pipes’ weightlessness simplifies transportation and installation, thus resulting in significant cost savings. Besides, their seamless design does not cause leaks during natural gas transmission, enhancing delivery systems’ safety. To sum up, PE gas pipes are an advanced way of directing natural gas flow through numerous industrial sectors.
Common Applications of PE Gas Pipes
Their resilience and efficacy have made PE gas pipes familiar in different industries where they are used.
- Residential Distribution: For instance, PE pipes are popular for residential connections between homes and main supply lines for natural gases, which allows people to enjoy heating, cooking, or hot water.
- Commercial and Industrial Use: In commercial buildings and industrial facilities, PE gas pipes distribute natural gases for use in heating, powering equipment, and other operational necessities, thereby providing a reliable source of energy in businesses.
-
Underground Transportation: These tubes are perfect for underground installations because they resist external pressures and factors related to the environment, hence representing a safe mode of tubing without rusting or leaking. These uses demonstrate how versatile and efficient polyethylene gas pipelines can meet the needs for supplying natural gases across diverse surroundings.
These uses demonstrate how adaptable polyethylene gas pipes are in meeting the needs of natural gas distribution across different settings.
Advantages of Using PE Pipes for Gas Distribution
While researching gas distribution, I discovered various essential advantages of using polyethylene (PE) pipes. Firstly, they are lighter than other materials, making it easy to handle and install them, thereby cutting labor costs and time spent fixing them, which I attach great importance to in all projects. Furthermore, the PE pipes have excellent corrosion resistance and stress cracking properties, allowing for longer service life and lower maintenance costs than traditional materials. Additionally, their flexibility allowed for more straightforward incorporation into current systems and withstanding changes in ground conditions without compromising integrity. Lastly, the smooth inside surface of PE pipes reduces friction, which helps increase gas flow speed, thus creating a more secure energy supply network.
How do you select the suitable PE pipe for your project?

There are many things to consider when selecting a suitable polyethylene (PE) pipe for your project. The first consideration is how it matches your distribution system’s diameter. This will give you an idea about its size and capacity, and if it is correct, it depends on the amount of gas you want to transport. Secondly, environmental factors such as soil type or potential ground movement should be assessed to identify a pipe with proper pressure ratings and flexibility. Also, consider what you will use it for; differentiate between residential and industrial items since these might need different standards being met by such items. Finally, ensure that local rules are not violated by checking those imposed by the industry so that your decisions meet safety requirements and performance criteria. The above considerations will help make effective choices when selecting an appropriate material for efficient gas dispersion.
Determining the Correct Pipe Size
The first thing I do is calculate the flow requirements for my project by looking at how much gas I need to move. For instance, in most cases, using online calculators provided by industry websites that match these figures with the appropriate pipe diameter is based on referring to gas flow rate (in cubic feet per minute). However, it’s good practice to consider pressure drop and how far the gas should go since these factors also affect size. I also searched for manufacturer specifications and guidelines because they usually have charts showing what size of piping one would use, given its flowing rates for various conditions. Lastly, any local code requirements governing safety and compliance will be reviewed before finalizing sizes. By so doing, I am sure I will get a tube size that guarantees the proper gas distribution through my system.
Comparing Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Differences between Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) include their properties, uses, and costs, among other aspects. As such, MDPE typically has a density within the range of 0.926 – 0.940 g/cm³, which gives it a balanced combination of flexibility and strength, which makes it suitable for low-pressure gas distribution or residential water pipes in most houses. Contrarily, HDPE has higher densities ranging from 0.941g/ccm³, making it more robust and more resistant to impacts, hence ideal for heavier-duty applications like industrial water or chemical pipelines.
Again, HDPE is widely preferred due to its ability to resist UV radiation and chemical corrosion, leading to a longer life span in harsh environments. At the same time, MDPE is often cheaper, particularly in projects where tight budgets are an issue. Finally, the selection between MDPE and HDPE depends on specifics such as pressure ratings required by the project at hand, environmental conditions prevailing around it, or even money setbacks that are there, including budget constraints in place.
Key Factors to Consider
Several significant issues influence my choice of the correct pipe materials for a given project. Firstly, I review system pressure needs, determining whether I select MDPE for low-pressure applications or HDPE for higher pressures. Secondly, I evaluate environmental conditions with HDPE resistant to UV degradation and chemicals appropriate in harsh atmospheres, while MDPE is best for moderate serviceability environments. Finally, there is also the budget to consider –HDPE offers long-term durability, whereas MDPE can be a cost-saving option, especially for budget-sensitive projects. These factors must be weighed before making an informed decision that meets performance and financial goals.
What are the Installation Procedures for PE Gas Pipes?

Safety and adherence to laws require various critical steps in installing polyethylene (PE) gas pipes. For instance, it starts with carrying out a complete site survey to establish how the pipelines should be routed, considering things like existing utilities and ground characteristics. Moreover, trenching must conform with local statutes by ensuring correct depth and width dimensions. Further careful attention is required when cutting pipes to the required lengths to prevent damage.
For instance, after cutting, joints may generally be fused or mechanically connected depending on the specific requirements of the project at hand. Consequently, before backfilling a trench, however, presser testing should first be carried out to check if any joint fail or leakages occur during the pipe installation process and if overall systems integrity exists before backfilling occurs. Finally trench tops can now be filled up ensuring that pipes are appropriately compacted so as not sink later . Regular inspections and safe handling procedures are necessary during the installation of the gas distribution system, keeping its reliability and safety intact till completion.
Preparing for Installation
Proper preparation is of great importance before installing PE gas pipes. First, ascertain that all necessary permits and inspections are in place per local regulations. Gather materials required, including appropriate PE gas pipe types, fittings, and fusion equipment. Additionally, an installation plan should clearly outline the project timeline and safety precautions. Assess the risks to identify potential hazards and set up procedures for dealing with them. Finally, it is vital to ensure that everybody involved in the installation has been properly trained on handling PE materials and they know how to install the pipes according to the guidelines provided. By taking these preparatory steps, we can smoothly progress through the installation process.
Steps for Proper Installation
I employ a systematic approach while installing PE gas pipes to ensure quality work and safety measures. Initially, I collect all needed tools and materials, such as PE pipes, fittings, and fusion equipment. Furthermore, I carefully develop a trench by determining its depth and width requirements as local codes prescribe. Then, I cut these tubes to size, avoiding any mistakes during this process. Subsequently, joints are either fused or connected mechanically, depending on project specifications. Before backfilling the trench, however, pressure tests must be conducted to maintain system integrity. Finally, proper compaction around the pipes is done during the backfilling of that trench while scheduling regular checks to ensure safety and reliability in our entire gas distribution system construction projects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inadequate Preparation: One of the significant errors is poor preparation for the installation site, which does not include checking for existing utility lines. Utility locates are essential to avoid damaging buried services, which can result in expensive repairs and project delays.
- Ignoring Manufacturer Guidelines: Many installers overlook the special guidelines provided by pipe and fitting manufacturers. Such neglect can lead to wrong fusion or installation techniques that ultimately undermine gas system integrity.
- Skipping Pressure Testing: Failing to do a pressure test before backfilling constitutes a significant mistake. This stage is crucial as it ensures no leakages and firm connections have been made. When this step is omitted, dangerous situations and future failures may occur because of system malfunctions.
What Fittings and Accessories Are Needed for PE Gas Pipes?
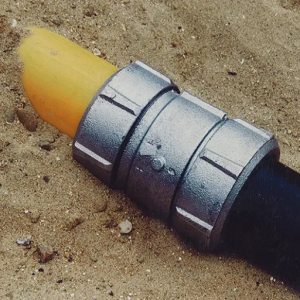
When dealing with polyethylene (PE) pipes meant for gas supply, several fittings must be included in their proper installations, such as:
- Couplings: Join two pieces of the tube together, ensuring a tight bond to prevent leakage.
- Elbows: Required when redirecting the line from one direction to another, elbows are available in various angles, such as 45° or 90°.
- Tees: Provide an efficient means of branching off into another line through which optimal distribution can occur.
- Reducers: Help shift among different sizes of tubes while maintaining smoothness in flow
- Valves: Key in controlling gas flow and providing emergency shut-off features.
- End Caps: These are fixed at the end of a pipe run when further extensions are not required.
- Mechanical Connectors: They are handy when joining two PE pipes without recourse to fusing procedures, especially during repair cases.
- Pipe Supports and Hangers: Ensure that the gas line remains stable with no movements under pressure situations
Apart from these fittings, always ensure that any accessories used are compatible with PE piping materials and meet local code requirements for safety reasons and durability considerations.
Types of Fittings for PE Gas Pipes
Polyethylene (PE) gas pipes have different types of fittings that I always think about with the various essential categories of gas distribution systems. The first one is compression fittings, which offer a process of easily connecting pipes without heat fusion. Another group comprises butt fusion fittings which make durable joints by heating and joining pipe ends. The rest includes electrofusion fittings, using electric current to heat coils inside the fitting for a quick bond between the pipe and fitting, flanged fittings for connecting pipes to valves, or other equipment that might be necessary. It is crucial to choose the right fit because it affects the integrity and safety of the gas system.
Using Transition Fittings
When it comes to transition fittings used in polyethylene (PE) gas pipe systems, these connectors are essential in connecting PE pipes with other materials such as metal or PVC. Transition fittings are designed in such a way as to allow for variations in diameter sizes or pipework material type, hence ensuring a secure joint with no leakage problems. Furthermore, all these types of accessories must adhere strictly to local standards since they interact with pressures and temperatures characteristic for this particular network of gas-supplying pipelines, thus causing me to be very cautious about mounting them correctly, irrespective of their threading works on metallic conduits or applying appropriate glues on plasticized PVC tubes due to proper installation’s significance regarding preserving the overall structure of a fuel transport mesh.
Importance of Proper Fittings in Gas Distribution
Safety, efficiency, and reliability depend on correct and proper fitting applications within gas distribution areas. Leaks can be prevented by selecting suitable pressure-rating fittings materials according to industry standards. We should not forget that unsafe installations may result in various failures caused by inappropriate connections, among others leading towards catastrophic failures as per the American Gas Association, while pointing out the importance of quality assurances besides adherence to local regulations at stake where sites like National Association Regulatory Utility Commissioners show how lower maintenance costs can be realized through practical application correct tools like joint failure risks reduction helps increase life span. Lastly, the expert installation of fittings that optimize performance and enhance overall system efficiency linked to safe gas transportation is one of the major themes highlighted on manufacturing websites such as Victaulic.
How to Maintain and Inspect PE Gas Pipes?

Regular inspections and maintenance procedures must be carried out to ensure the reliable performance and longevity of PE (polyethylene) gas pipes. It is important to regularly make visual observations to find the most minor signs of damage, such as dents, cracks, or scratches. One should also be keen to watch out for any changes on the surface or soil displacement around the buried ones. To detect leaks that may not be visible, periodic pressure testing has been used in underground installations. Furthermore, all instructions the manufacturer provides for cleaning and maintaining joints and fittings must be strictly adhered to to prevent contamination. There are some standard rules about controlling these systems; they include having a routine inspection schedule and keeping accurate records of all their activities.
Routine Maintenance Tips
A good habit I have developed is conducting frequent visual inspections where I check for signs of abrasion, like cracks or dents. Moreover, I continuously scrutinized how the ground behaves near pipes hidden in it to know if any new inexplicable movements appeared from shifting. After this, I periodically test the system’s capability to sustain its specified pressure. At the same time, hidden leaks can still occur on different occasions, an action that has been helpful regarding my safety measures. In addition, one should follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding cleaning pipe joints and fittings to avoid contaminating them with dirt or other substances that could affect their functionality. Lastly, maintaining a logbook clearly showing my various inspection activities and related checks performed will enable me to remain aware of whether the system remains dependable with time.
Inspection Procedures
PE gas pipe inspection methods consist of visual evaluation combined with technical examinations. Begin by visually inspecting every section comprehensively so that any apparent defects like fractures, bulges, or worn areas are identified easily at a glance. You need to monitor connections and seals for leakages or evidence that wear around these parts is underway. For instance, you may have to dig out buried lines to ensure the pipe and soils around it remain intact. Therefore, when running your ordinary procedures, perform some pressure testing from time to time to ensure that a system can bear its pressure even with no leakage. Also, if possible, employ such non-destructive testing approaches as an ultrasonic or electromagnetic inspection that can reveal any latent problems not apparent during the visual survey alone. Lastly, all findings and actions taken during an inspection should be recorded in a maintenance logbook for future reference to maintain compliance and improve the overall safety of gas distribution.
Signs of Wear and Tear to Watch For
When examining PE gas pipes, it is vital to look for specific wear indicators. These include:
- Cracks and Fractures: Pipes with visible cracks pose a danger as they may leak. Inspect both the surface area and joints thoroughly, checking for any form of cracking.
- Bulges and Deformations: A pipe that has bulged or is not shaped correctly may indicate internal pressure problems or external damages. Such deformations may obstruct the system’s overall performance and safety.
- Corrosion and Discolouration: Although these pipes resist corrosion, any change in color or surface deterioration denotes chemical reactions or damage, which could lead to failure.
- Ground Movement: Unusual soil movements around buried pipes can shift their position and stability, making them prone to breaks or leakage.
- Leakage: The smell of gas or the sight of bubbles emanating from the area surrounding the piping should be dealt with immediately because they are obvious signs of potential leakage.
Being on high alert for these factors ensures the long life and safe operation of your PE gas pipeline system. Regular checks and prompt attention to anything wrong will save you from expensive repairs and dangerous situations.
Are There Safety Concerns with PE Gas Pipes?

Even though polyethylene (PE) gas pipes are generally considered safe and capable of resisting various forms of damage, some safety concerns must be addressed. One such problem is stress cracking, which can occur due to environmental conditions or improper installations done on them. In addition, although they have low susceptibility to corrosion, PE pipes can get damaged by prolonged exposure to certain chemicals over time and high-temperature extremes. Hence, proper monitoring processes must be employed through regular comprehensive inspections to detect wearing out, mitigate risks from ground movement, and maintain jointing integrity in fittings, among others. Additionally, strict compliance with regulatory guidelines while following best practices significantly enhances safety and reliability within PE gas piping systems.
Safety Standards and Certifications
It is essential to follow specific safety standards to ensure the safety and reliability of polyethylene (PE) gas piping systems. I understand that some organizations like the American Gas Association (AGA) and the Institute of Gas Technology (IGT) guide these systems’ design, installation, and maintenance. Some certifications, such as ASTM F2620, are beneficial as they guide PE pipes’ heat fusion joining, thus ensuring joint integrity and preventing leakages. By following these regulations and being aware of best practices, I can guarantee that the P.E gas piping systems I use attain the highest level of safety while functioning effectively under various environmental conditions.
Preventing Leaks and Breaks
In polyethylene (PE) gas piping systems, proactive measures must be taken to prevent leaks and breakages at all times. For instance, according to many players in this field, regular inspections and maintenance are essential first steps. An ordinary monitoring program would also help identify wear signs or corrosion that could occur early enough. Joint failure risks can be reduced if the correct installation method is used, such as keeping the fusion temperature correct or following manufacturer instructions properly. It is also good to consider environmental factors like ground movement or temperature variations when using appropriate backfill material, which may add some support. Lastly, training staff on best practices and emergency response protocols enhances system integrity; hence, comprehensive learning plus compliance with industry requirements cannot be overemphasized.
Emergency Procedures for Gas Line Issues
Whenever a gas line emergency occurs, my immediate concern is everyone’s safety near where I am. I begin by clearing all employees from the vicinity while directing them towards more secure areas. I must call in emergency services and the utility company immediately. The risk of triggering any probable leakages has necessitated no use of electronic devices, including sparking tools. Also, ensuring clear access points for emergency responding agencies’ prompt assessments becomes very important since they are emergency responders. After handling the immediate urgency, a thorough investigation is needed to establish what brought about the problem so that there can be improvements in maintenance and response protocols in the future. This approach is a way of further reducing risks while my commitment to safety is reinforced.
Reference sources
- Natural Gas Distribution Solutions with PE Pipe – WL Plastics
- DriscoPlex® 6500 Series PE Piping – Chevron Phillips Chemical
- 4″ IPS SDR11.5 PE2708 Yellow MDPE Gas Pipe Straight – HDPE Supply
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a polyethylene gas pipe?
A: A polyethylene gas pipe, often called PE gas pipe, is a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe specifically designed to convey natural gas and propane. It is commonly used in underground gas distribution systems due to its durability and flexibility.
Q: Why is the PE2708 pipe considered an excellent choice for natural gas distribution?
A: PE2708 pipe is an excellent choice for natural gas distribution because it meets the ASTM D2513 standard, is highly chemical and environmental stress resistant, and is lightweight and easy to install. The pipe is also yellow for easy identification.
Q: What are the benefits of using underground gas pipes for natural gas distribution?
A: Underground gas pipes provide several benefits, including protection from environmental damage, increased safety by reducing the risk of accidental punctures, and longevity due to their corrosion resistance. This makes them a reliable option for natural gas distribution systems.
Q: Can polyethylene pipe be used for natural gas and propane distribution?
A: Yes, polyethylene pipe, including yellow MDPE, is suitable for natural gas and propane distribution. It is designed to effectively handle the pressure and chemical properties of both gases.
Q: What is the purpose of a riser in an underground gas pipe installation?
A: A riser is used to transition the underground gas pipe to an above-ground connection. It provides a safe and secure way to bring the gas pipe to the surface for connection to appliances or meters.
Q: How should polyethylene gas pipes be stored outdoors?
A: Polyethylene gas pipes should be stored outdoors to protect them from direct sunlight and physical damage. To prevent degradation from UV rays, they should be kept in their original packaging or covered with a UV-resistant tarp.
Q: What is the difference between CTS and IPS in polyethylene gas pipes?
A: CTS (Copper Tubing Size) and IPS (Iron Pipe Size) refer to polyethylene gas pipes’ different outside diameter standards. CTS is typically used for smaller-diameter pipes, while IPS is for larger ones. The choice between CTS and IPS depends on the application and system requirements.
Q: Why is it essential to chamfer the ends of a polyethylene gas pipe before installation?
A: Chamfering the ends of a polyethylene gas pipe is essential to ensure a smooth and secure fit when joining pipes and fittings. It helps prevent pipe damage and provides a tight seal, reducing the risk of leaks in the gas distribution system.
Q: Are any specific related products needed to install a polyethylene gas pipe system?
A: Yes, installing a polyethylene gas pipe system may require related products such as fittings, risers, chamfer tools, and pipe fusion equipment. These items are essential for ensuring a secure and reliable gas distribution system.
Q: How does high-density polyethylene (HDPE) compare to other materials like iron pipe for gas distribution?
A: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers several advantages over traditional materials like iron pipe for gas distribution, including superior flexibility, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation. HDPE is also lighter, which makes handling and transportation more accessible, and it can be fused to create leak-free joints.






