Drainage infrastructure plays a critical role in modern construction, agriculture, and urban development, ensuring efficient water management and long-term durability. Among the various materials available today, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) corrugated pipes are rapidly emerging as a game-changer in this field. Lightweight yet incredibly durable, these pipes offer unparalleled versatility and cost-efficiency, making them an ideal choice for projects of all sizes. This article explores why HDPE corrugated pipe solutions are reshaping the drainage industry, highlighting their unique properties, applications, and contributions to sustainable construction practices. Whether you’re an engineer, contractor, or project planner, discover how HDPE corrugated pipes can transform your approach to water management.
Introduction to HDPE Corrugated Pipe

What is HDPE Corrugated Pipe?
An HDPE corrugated pipe represents a lightweight and durable choice of piping, mainly devised for drainage systems and water management applications. The HDPE is itself a thermoplastic polymer known chiefly for its good strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and long life. The pipe is constructed with a corrugated wall for structural strength with a smooth interior to provide effective flow of water, making it applicable for residential as well as industrial projects.
Environmental resistance is a major attribute of an HDPE corrugated pipe. It holds up under extreme temperatures, chemical assaults, and high-pressure systems of flow that might degrade its performance. Such properties ensure that the HDPE pipes retain their long-term reliability, whether installed in difficult or high-stress environments like under highways or under areas that experience a lot of soil movement.
Given its uses, it is employed chiefly for stormwater drainage, agricultural irrigation, sanitary sewers, and culvert installations. Being lightweight in construction, it reduces the transportation and installation costs and thus leads to sustainable construction practices. HDPE corrugated pipes present a more cost-effective and environment-friendly alternative to concrete or metal for engineers, contractors, and planners alike.
Key Features of HDPE Corrugated Pipe
- Durability and Flexibility: HDPE corrugated pipes are very durable and resistant against external forces, such as heavy loads or ground movement. The pipes require minimum maintenance because of their flexibility in light installation on uneven terrains and in areas prone to soil displacement.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: They have high resistance to chemical action and corrosion and serve best in places where exposure to aggressive chemicals is common. Being noncorrosive, HDPE adds more life to the piping system than metal ones.
- Lightweight Construction: Being lightweight, HDPE corrugated pipes can save considerable handling and transport charges. This feature helps to install them in a quick time, thus reducing the labor effort and overall project deadline.
- Hydraulic Efficiency: The smooth streamlining of water within the pipe ensures hydraulic efficiency offered by HDPE corrugated pipes, thereby serving well for stormwater drains, irrigation schemes, and sewers with minimum interfacing losses.
- Environmentally Sustainable: HDPE corrugated pipes are recyclable and are usually produced in ways that reflect environmental consciousness. Their lifespan is probably the longest among pipes, thus reducing the environmental impact due to frequent replacements, thus promoting green construction.
Meeting the growing demand of modern infrastructure for practical solutions and environmental values, HDPE corrugated pipes, being strong yet flexible and economical, continue to be the preferred choice throughout various industries.
Benefits of Using HDPE Corrugated Pipe
- Durability and Longevity: HDPE corrugated pipes resist chemical corrosion, abrasion, and environmental stress cracking. They have a service life of more than 50 years if the installation is conducted under normal conditions. These pipes’ ability to resist depredation by harsh environmental conditions renders them suitable for all long-term installations.
- Still More Lightweight and Easy Installation: Being lighter in structure, HDPE corrugated pipes are easier to transport, handle, and install compared with traditional materials like concrete and steel pipes. This reduces the amount of labor hours, requirements on heavy equipment, and project time, thus assuring a swift installation.
- Hydraulically Very Efficient: Smooth inner walls of HDPE corrugated pipes reduce frictional resistance, thus increasing hydraulic efficiency. This hydraulic advantage allows for greater flow capacity at diameters smaller than those of conventional pipes, thus saving on cost and material.
- Environment-Friendly and Recyclable Material: Recognized as recyclable, this product is generally manufactured in an environmentally friendly fashion, thus forming an integral part of the green construction concept. Its lengthy service life also means that the downtimes for replacement are less frequent, thereby slashing the environmental impact of construction projects.
- Highly Flexible and Adaptable: The inherent elasticity and flexibility make HDPE corrugated pipes an ideal choice for installation in areas having unstable or shifting soil conditions. They absorb ground movement without being cracked or ruptured and still ensure reliability in adverse environments.
Comparative Analysis of Piping Materials

HDPE vs. PVC: A Detailed Comparison
HDPE offers flexibility and resilience coupled with UV resistance, and hence may find its use under high pressure and extreme scenarios, while with PVC, there’s rigidity and economy of cost, thus suited for static applications.
|
Aspect |
HDPE |
PVC |
|---|---|---|
|
Composition |
Thermoplastic |
Vinyl Polymer |
|
Flexibility |
High |
Low |
|
Strength |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
UV Tolerance |
High |
Low |
|
Temperature Range |
-40°F to 140°F |
Limited |
|
Connection |
Heat Fusion |
Cement/Gasket |
|
Pressure Capacity |
High |
Moderate |
|
Curvature |
Tight |
Wide |
|
Expense |
Higher upfront |
Lower upfront |
|
Usage |
Dynamic, high-pressure |
Static, low-pressure |
|
Longevity |
100+ years |
Shorter |
Advantages of HDPE Over Concrete Pipe
- Lightweight and Easy to Handle: HDPE pipes pose a markedly lighter option compared to concrete pipes in terms of transport and installation. Industry figures show HDPE pipes to be up to 90% lighter than concrete pipes; such being the case, installations can be speedier and are not as demanding on heavy machinery.
- Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: HDPE pipes provide corrosion protection in addition to resistance to a wide range of chemicals, in contrast to concrete pipes. This makes them suitable for applications where acidic or alkaline environments may exist, rendering the concrete somewhat susceptible to degradation and eventual failure.
- High Durability and Longevity: Depending on the working environment, the lifespan of HDPE pipes ranges between 50 and 100 years. Concrete pipes tend to develop cracks and structural weaknesses over time, especially due to freeze-thaw actions. HDPE retains its structural integrity well through such challenging situations because of its flexibility and strength.
- Leakage Prevention and Water Tightness: Unlike concrete pipes that provide segmented or gasketed connections, HDPE pipes are joined by welding to almost seamless joints that are truly watertight, thereby ensuring superior leakage prevention. This will reduce water losses in initiating water supply systems and other such applications, thereby improving efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness in Long-Term Applications: At times, concrete may appear to be cheaper initially. In the long run, however, the lesser requirement for labor, installation, and maintenance does prove to be a definite advantage for HDPE. There are studies proving that HDPE-based systems turn out to be 25-30% cheaper on a 50-year term when aggregate factors have been included.
There are key areas in which HDPE corrugated pipes furnish a strong and efficient alternative to concrete piping systems.
Performance of Corrugated HDPE in Various Applications
Corrugated High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes tend to perform well all over the application spectrum because of flexibility, strength, and resistance to external or internal influences. Among the most important applications are in stormwater management systems, where HDPE pipes carry water with maximum hydraulic efficiency. With their smooth internal surface, HDPE pipes, unlike pipes of conventional materials, present the least frictional resistance and thus allow flow at maximum rates even under heavy loading.
Also, agricultural drainage applications benefit a lot from these non-corrosive HDPE pipes that operate well under the frequent presence of corrosive chemicals or acidic soil conditions. The lightweight nature of HDPE pipes ensures faster installation and less equipment and manpower resources, thus translating into improved project times and cost efficiencies.
Such systems of handling high-pressure systems coupled with highly aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures show the best applications for HDPE corrugated pipes. Laboratory tests have established that HDPE withstands such environments while maintaining its structural integrity far beyond the design life afforded by other conventional materials.
Finally, abrasion resistance and resistance to root intrusions make HDPE pipes a choice solution for residential and commercial sewage systems requiring long-term maintenance or operation with limited upkeep. According to numerous field tests and comparative analyses, when pitted against alternative materials under identical conditions, HDPE appears to outperform; this versatility lends to its importance as a present-day infrastructure solution.
Applications of HDPE Corrugated Pipe

Use in Drainage Systems
Corrugated pipes made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are used widely in different drainage applications because of their durability, flexibility, and lower cost. These pipes fare well when the design is geared toward strength and resistance to environmental factors. Below are five major drain system applications of the HDPE corrugated pipes:
- Stormwater Management: HDPE corrugated pipes work in stormwater management to direct runoff and drain flood risks. With a smooth interior surface, these pipes allow high water velocity; whereas the corrugated exterior gives them structural stiffness to withstand severe flow rates combined with heavy loading. Studies have shown that the flow coefficient of these pipes, i.e., Manning’s n value, can drop as low as 0.009, which means it offers superior hydraulic efficiency.
- Subsurface Drainage: These are important pipes for drainage in agricultural fields and sports fields zones where the excess water level needs to be controlled. These pipes, HDPE, are resistant to chemical and corrosion caused by water and are therefore suitable for long-term installation of drainage in a wetland environment. The flexibility of these pipes also favors their laying where terrain requires curving or uneven adjustments.
- Highway and Road Drainage: HDPE corrugated pipes act as culverts and conduits below roads and highways that allow for good drainage and hence enhance the life of the roadway.
- Leachate Drainage of Landfill: At waste treatment centers, these pipes serve the purpose of collecting and conveying leachate safely. Their chemical resistance is such that they are not subject to degradation by the hazardous compounds normally found in landfill-type environments, ensuring safety in operation and system durability.
- Residential and Commercial Drainage Systems: HDPE pipes form the core of residential drainage and foundation systems, which guard iagainst nfiltration of water and enable the protection of structural foundations. An easy solution to install in limited working space, plus an extended life of the system, makes them a viable solution for both heavy and light construction projects.
All these applications emphasize the responsive quality of the HDPE corrugated pipes toward various drainage problems and their unequalled reliability and efficiency across industries.
Role in Agricultural Infrastructure
In agricultural infrastructure, the HDPE corrugated pipe optimizes water management before it can be ensured for crop production and may contribute to soil amelioration. These pipes are generally used in subsurface drainage mechanisms wherein micro-managing the flow of excess water from topsoil prevents the waterlogging situation that may prove detrimental to crops with respect to root development and nutrient uptake. Being lightweight and flexible allows the fast deployment of these pipes across large farmlands, even in undulating terrains, thereby reducing the cost of labor and time in installation while maintaining operational efficiency.
In irrigation systems, these pipes discharge water under the intended pressure and meet the irrigation requirements of the crops so as to reduce wastage. These pipes also bear chemical corrosion and do not easily allow the deposition of sediments, thereby providing the assurance of long-term functioning and flow rates that are needed for the sustainability of agriculture. These pipes are also suitable for flood protection as they provide a way to channel the excessive runoff from farmlands during heavy rain, thus keeping the crops safe from damage.
In my opinion, HDPE corrugated pipes are immensely versatile in supporting modern agriculture. The long endurance and adaptability of these pipes render them capable of truly addressing various problems-from soil drainage to high-efficiency irrigation. Through its use, it turns into an aid for improving agricultural production and promotes sustainable water resource management matter which is a key matter to tackling global food security. Hence, it counts among the essentials in agricultural infrastructure.
Innovative Uses in Construction Projects
The integration of cutting-edge materials and design methodologies into modern construction has led to seldom-seen applications in special piping systems. For example, HDPE pipes have become the norm, with usage due to their corrosion resistance, chemical stability, pressure resistance under pressure variation, and metal barrier property. These pipes go into highly developed drainage systems engineered to prevent the flooding of urban areas and enhance water management in highly populated regions.
On the other hand, flexible piping systems like PEX have changed plumbing by allowing for good-working installers, thus reducing labor costs and project time. These advanced pipes have also been used in geothermal heating and cooling systems to efficiently transfer heat with minimal energy loss, all of which goes along with the push for energy sustainability in construction.
A few of the most recent advancements surely include new systems with sensors that monitor fluid flow, pressure, and temperature in real-time. These systems provide usable data to adjust maintenance intervals for longer system life and higher operational efficiency.
These alternative applications consider the immediate requirements of a construction project, but they also consider the long-term aims of energy efficiency, sustainability, and resiliency. In so doing, based on strong and flexible piping systems, the construction industry continues to evolve, ensuring the creation of infrastructures that will stand against environmental and logistical trials.
Installation and Maintenance of HDPE Pipe

Best Practices for Installing HDPE Corrugated Pipe
An appropriate installation of an HDPE corrugated pipe is critical to maximize its performance over time and to give it structural integrity and resistance to environmental stress. The best practices given below summarize the key steps and considerations to obtain a good-quality result:
- Site Preparation and Trench Design: Initially, the site needs a detailed evaluation to establish the characteristics of the soil, the level of groundwater, and the load imposed. This trench for HDPE pipe installation has to be of a base with a solid foundation fixed with a set grade level following the design slope. The trench width must be wide enough for the backfill material to be adequately compacted on either side, normally 1-1/2 times the diameter of the pipe.
- Bedding Material Specification: A good, clean, granular bedding layer must be applied to give proper and uniform support to the pipe. Hence, bedding could be of crushed stone or gravel. The thickness of the bedding layer will generally range from 4 to 6 inches. Never use any organic materials, nor soil with a high clay content; such materials will impair drainage and structurally weaken the pipes.
- Pipe Placement and Alignment: HDPE corrugated pipes should be handled with care during transportation and installation in order to limit damage. Lower the pipe into the trench; do not drag it. Care must be taken to ensure that joints are aligned properly and connections are made according to the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid leakage or misalignment.
- Backfill and Compaction: Backfill material should be placed uniformly in layers, with each layer not exceeding six inches in depth. The compaction of each layer should be done through mechanical compaction equipment or hand tamping, especially around the haunches of the pipe, as this is an important area in supporting the vertical and lateral loads. Compaction must be at least 90% of Standard Proctor Density to provide adequate support.
- Joint Testing After Installation: Pressure or infiltration testing (as applicable) should be carried out after the installation to ascertain the integrity of the pipe joints and to detect any possible leakages.
- Inspection and Documentation: Visually inspect the pipes for any deformation or irregularities after the installation. Also, maintain documentation of photographs, pressure test results, and as-built drawings for record keeping, contractual compliance, and future reference.
The team responsible for installing the project will greatly benefit from these installation best practices to ensure that the HDPE corrugated pipe system works efficiently under operating conditions for which it was intended. Adherence to these practices will eliminate many premature failures of the HDPE pipe and enhance its longevity and reliability as an infrastructure system.
Maintenance Tips for the Longevity of HDPE Pipes
Periodic maintenance is the best way to prolong the life of HDPE corrugated pipes. Below is an account of specialized tips considered for paramount operational efficiency:
- Periodic Visual Inspection: Periodical assessment of the pipeline system shall be fostered at points susceptible to wear-out, like joints, connections, and high-pressure zones. Surface deformation, abnormal wear, or even dislodgment, when observed in the early stages, can forestall expensive failure.
- Clean and Clear Debris Often: Through the accumulation of sediment or debris, the flow ends up being impeded, and internal pressure mounts. Clean the pipes by any safe means, such as low-pressure water jetting or foaming pigging, to ensure the way is clear without damaging the pipe walls.
- Evaluate Thermal and UV Exposure Risk: HDPE pipes are, indeed, highly resistant to environmental stress; yet, long exposure to UV rays or abnormal temperature variations can eventually degrade the material. Put protective coatings or shrouds onto the pipes exposed to direct sunlight; insulate the pipes where frost or extreme heat is a threat.
- Monitor for Chemical Compatibility: Continually check that the substances transported are compatible with the HDPE material. The chemicals may overcome the resistance levels of the HDPE and cause softening, cracks, or even the compromise of pipe integrity. Maintain an updated chemical exposure log to cross-reference against operational changes.
- Pressure Tests and Flow Monitoring: Conduct pressure tests periodically to locate any leaks, weaknesses, or inefficiencies present in the pipeline, perhaps by means of flow rate sensor integration and keeping track of the performance parameters continually, giving a clear indication of blockages or pipe wear.
- Repair Protocols: Repairs shall be undertaken in line with all industrial regulations, whether welding or coupling techniques. Always record and document every step in a repair to allow for complete traceability and audit compliance.
The blending of these maintenance strategies into routine operations will reduce unscheduled downtime, thereby increasing pipeline operational lifespan while also providing an adequate level of environmental and safety compliance.
Environmental Sustainability of HDPE Corrugated Pipe
Recyclability of HDPE Material
HDPE micro, widely known for its superior recyclability, has become an essential tool in the practical realization of sustainability within various industrial sectors. HDPE is categorized as Type 2 resin; hence, it can be reprocessed with minimal degradation to its intrinsic qualities. Allowing other products to be made from waste, the recycling process involves washing HDPE, shredding, and then remelting it into pellets called recyclate.
There has been a continuing improvement in HDPE recycling rates in recent years, and it enjoys wide applications in piping, containers, and composite materials. Today, there is recycled content in possibly 30% of HDPE products used globally. Recycled HDPE, thus, saves on virgin resin requirements derived from fossil offerings and could decrease greenhouse gas emissions by 50%-70% due to the considerably lower energy requirement in production as compared with virgin HDPE. The closed-loop cycle thus plays a considerable role in carbon reduction and goes hand in hand with stringent environmental legislations.
Furthermore, owing to HDPE’s resistance to chemical attack and abrasion-resistant wear properties, recycled-based products are just as strong and durable as those made with virgin HDPE. Various municipalities and industries are cooperating to upgrade collection and processing infrastructure toward maximizing HDPE circularity. Full-fledged and modern process technologies, e.g., near-infrared spectrometry, serve to improve the purity of HDPE recyclate by effectively removing contaminants from the waste streams. With such technologies in the fold, it would be scalable on a worldwide level, as is HDPE recycling, with a vision for a sustainable future.
Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing Processes
Energy conservation in manufacturing processes has become a matter of utmost consideration for industries worldwide, owing to the commercial reasons of cheaper plant operations and sustainability. The more advanced and modern energy-efficient measures truly allow minimal energy consumption while maintaining productivity. For example, the use of VFD in motorization allows improved control over energy utilization, thereby reducing its cost as well as the emission of greenhouse gases. These energy-efficient solutions find immense importance in industries that consume heavy energy, such as steel, chemical, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Besides, energy management frameworks across manufacturing sites have found a facelift by virtue of data-driven mechanisms. Combining IIoT sensors with intelligent monitoring platforms facilitates the real-time energy analysis of equipment so that facilities can promptly find inefficient processes and fix them. Energy audits powered by machine learning algorithms are more commonly used to detect hidden inefficiencies and predict trends in energy usage, thereby enabling decision-making based on foresight. In addition, the energy wastage is reduced by the integration of predictive maintenance in equipment operations to ensure machinery runs at optimal levels and prevents unscheduled downtime.
Looking at large-scale energy-efficiency accomplishments, more sectors are leaning toward integrating renewable energy, followed by the integration of waste-heat recovery. Solar PV plants and wind turbines assist the plants with partial or complete green energy, whereas technologies such as CHP help to capture and utilize thermal energy produced during production processes. Aggressive chasing of decarbonization strategies hence stands on a firm foundation laid by the interplay of these technological innovations, regulatory policies, and sustainability targets.
Impact on Sustainable Infrastructure Development
The infrastructural focus on sustainability has led to tangible improvements across many spheres, each designed to reduce intrusion on sustainable development while increasing efficiency, resilience, and social good. Below are five specific areas that exert sustained pressure on the development of infrastructure toward a more sustainable future:
- Energy-Efficient Building Design: Renewable and clean energy technologies like photovoltaics and geothermal systems helped reduce energy consumption by 25-40% when used in new construction projects. Additionally, energy-efficient appliances and building-related materials, advanced insulation in particular, make for cost savings down the life cycle of buildings and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Management and Recycling Initiatives: Use of construction materials from recycled sources, for example, steel and concrete processing, increased by 19% during the last five years. Such practices divert potentially millions of tons of waste away from landfills every year, keeping in line with the broader objectives laid down under the circular economy.
- Green Transport Systems: Investments for green transport for emission reduction include electric buses and urban rail, which have reduced urban air pollution significantly. In a few other cities around the world, conversion to electric public transit has resulted in a 50% reduction in CO2 emissions vis-à-vis conventional diesel-powered counterparts.
- Water Resource Optimization: Water-saving technologies are becoming increasingly common in infrastructure development, where water efficiency has been improved by 30%, including smart water systems and rainwater harvesting. This is particularly important in areas falling in the category of arid and semi-arid, where water scarcity becomes a grave issue to be tackled.
- Smart Cities and IoT Integration: IoT adoption in smart cities allows real-time monitoring and management of ICT for energy, water, and waste. These data-driven insights have supported resource allocation and sustainability decisions, with cost reductions of around 20% reported alongside better environmental indicators in certain smart cities.
Remains in innovation and smart planning while building megastructures capable of adapting their constituents to the challenges faced currently and shortly.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an HDPE corrugated pipe?
A: An HDPE corrugated pipe is a type of pipe made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that features a corrugated outer wall and a smooth inner wall. This design provides enhanced structural integrity and hydraulic performance, making it ideal for various applications, including storm drainage and drainage systems.
Q: What are the advantages of using a corrugated HDPE pipe?
A: Corrugated HDPE pipes offer several advantages, including corrosion and abrasion resistance, impact resistance, and high toughness. They are lightweight, easy to handle, and can withstand various environmental conditions and traffic loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Q: How are HDPE corrugated pipes manufactured?
A: HDPE corrugated pipes are manufactured through a process that involves extruding high-density polyethylene into a corrugated shape. This results in a pipe with a larger pipe diameter and a unique design that enhances its structural stiffness according to standards set by organizations like ASTM International and AASHTO M252 and M294.
Q: What is the difference between dual-wall and single-wall HDPE pipes?
A: A dual-wall HDPE pipe features an outer corrugated wall and a smooth inner wall, providing superior hydraulic performance and structural strength. In contrast, a single-wall pipe only has a smooth or corrugated wall. Dual-wall pipes are often preferred for drainage applications due to their increased durability and resistance to structural failure.
Q: What pipe specifications should I consider when selecting an HDPE corrugated pipe?
A: When selecting an HDPE corrugated pipe, consider the pipe size, wall thickness, pipe stiffness (SDR), and the specific application requirements. It’s essential to evaluate the hydraulic performance and the connection method to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Q: Can HDPE corrugated pipes be used for storm drainage?
A: Yes, HDPE corrugated pipes are widely used for storm drainage applications. Their design allows for efficient water flow while maintaining strength under varying environmental conditions. They can effectively transport water into the pipe and prevent flooding in urban areas.
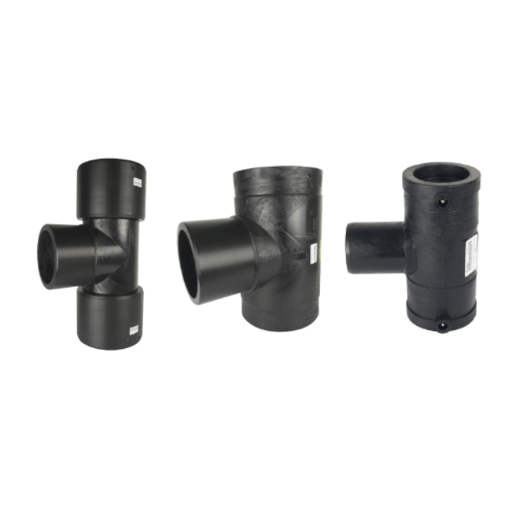
Q: What types of fittings are available for HDPE corrugated pipes?
A: Various pipe fittings are available for HDPE corrugated pipes, including elbows, tees, and couplings. These fittings are designed to create secure connections and accommodate different pipe sizes and configurations, ensuring a leak-free system suitable for various applications.
Q: How does the impact resistance of HDPE corrugated pipes compare to other types of pipes?
A: HDPE corrugated pipes exhibit excellent impact resistance compared to other types of plastic pipes, such as polypropylene pipes. This toughness makes them suitable for applications where they may be exposed to heavy loads or potential impacts, reducing the risk of damage or structural failure.






