High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes have gained popularity in various fields due to their strength, adaptability, and affordability. Regardless of the intended purpose and period of operation of a structure, it is essential to know how to combine HDPE pipes to obtain a strong, tight, and leak-free joint. This guide will cover the most frequent methods of joining HDPE pipes, making the connection between the purpose and use of each technique and its advantages. Fostering such knowledge will help you understand the most reliable and efficient HIV joining techniques if you work on large civil engineering sites or rest on other small plumbing projects.
What are the Commonly Joined Methods for HDPE Pipe?
how is hdpe pipe most commonly joined?
The methods most commonly used to connect HDPE pipes are butt fusion, electrofusion, and socket fusion.
- Butt Fusion: This is where the ends of two thermoplastic pipes are brought together after softening and heating them, which melts them into a single bonded seamless pipe joint. It is suitable for large-diameter pipes and yields very high-quality and uniform joints.
- Electrofusion: Here, the ends of the pipes are joined using a unique coupling with embedded heating elements. Electrofusion is especially suited for applications with confined spaces or where smaller diameter pipes are to be adjoined, and accuracy is of the essence.
- Socket Fusion: This assists in the socket fusion of pipes and fittings. It similarly employs a heating tool to melt the pipe and the fitting, with the pipe inserted into the socket. This type of fitting is known to be reliable as it is employed with socket: sleeve fittings of small diameter pipe and fittings.
These procedures provide safety in linking two or more connections and durability, which makes them suitable for everyday use in all household plumbing systems and industrial systems.
Understanding HDPE Pipe Joining Methods
To obtain quick responses to the questions concerning HDPE pipe joining methods, we analyse three top-rated websites. These sources include Pipe Joining and Fabrication by McElroy and Integral Fusing and Pipe Performance by Chevron Phillips Chemical, which supplements each other towards the technical and practical aspects of butt fusion, electrofusion, and socket fusion systems.
- Butt fusion: As pointed out by McElroy, butt fusion is a common and generally accepted, and well-investigated method practiced elsewhere. The members to be jointed are placed in a butt fusion machine where a heater plate brings together the ends at specified temperatures until they cool beneath the pressure that was set up. Thin technical details encompass the heater temperature type prone to most builders’ wear (approx. 400°F), heating and cooling pressure, and alignment accuracy for good seam.
- Electrofusion: According to Integrity Fusion, electrofusion is in terms of fitting that has additional devices that heat. Rather than placing the core and pipe carrier in a fixture, they are put into an electrofusion processor where the current is used to melt the pipe surfaces and fit them together. Some of the critical variables are the fusion voltage and fusion time, which the fitting manufacturer specifies. Pipe preparation includes scraping off the oxidation layer from the pipe to leave a clean surface for the fusion.
- Socket fusion: Performance Piping states that socket fusion is the joining of thermoplastics by heating and softening the pipe, fitting it to the optimum temperature, and inserting the hot end-stop perfectly without a second rotation. This technique is somewhat operational to less favorable diameters for butt fusion. Parameters include the heating element temperature, generally set at around 2600F, and the controlled and timed heating and insertion that determine the reliability of the joint.
Such joining methods employ the accuracy and stability of temperature, pressure, and surface characteristics to produce strong, durable, and leakproof joints for piping systems.
Exploring Different Types of Joint Techniques
- Butt Fusion: As stated by the industry experts like McElroy (mcelroy.com), butt fusion is a rather complicated yet prevalent method of polyolefin pipe joining. Essential elements are the temperature of a heater plate, which usually varies between 400°F and 450°F, and the capability to sustain pressure at every heating and cooling stage to achieve strong bonding.
- Electrofusion: As Ferguson (ferguson.com) mentioned, electrofusion consists of fittings containing heating coils turned on by electricity. The fitting manufacturer sets parameters for fusion, which is vital to its success, including but not limited to voltage (usually around 40V) and time taken for the fusion process. It is also important to scrape the surface preparing processes as this removes the oxidized surface, a source of weak joints.
- Socket Fusion: Performance Pipe (performancepipe.com) recalls that socket fusion is ideal for smaller diameters and applies to melting both pipe and fitting materials, which occurs at about 500 °F heating. Our research from sources followed the position that there has to be stress on the correctness of angular position and time expense while inserting a plug in order to achieve a sound joint.
These abstracts, taken from resources on leading specialists, focus on the essence of precision with respect to the parameters of each method. For example, heat application, pressure application, or surface preparation are critically required if joints hold effectively and are durable.
Comparing Weld vs. Fitting Solutions
Weld solutions such as butt fusion and electrofusion aim at creating solid and reliable joints which require the management of other parameters, including heat and pressure. For example, the butt fusion method wants a heater plate maintained between 400′ and 450′. In the case of electrofusion, voltage settings must be kept, usually in the region of 40V, to switch on heating coils that are embedded to heat several materials.
Conversely, fitting solutions, as opposed to welded joints, often contain mechanical parts, and the installation may demand lesser on-site equipment. As such, they do not require so much time to set up. They are generally quicker and easier to deploy, especially in situations where welding is not possible or more flexibility is needed for maintenance purposes. Yet fittings may not provide such leakproofness as an effective weld to the affected zone.
The technical parameters that are considered very vital to these processes include:
- Butt Fusion: Plate heater temperature (4000F – 4500F) and proportional pressure during the heating phase and cooling.
- Electrofusion: Properly fixed voltage (approx. 40Volts) and proper frame fusing time according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
In the end, the choice between a weld or a fitting solution depends on the considerations needed for the application in hand: longevity, ease of use and installation, and exposure to the environment. Using reputable references, these comparisons are justified by the precision demand and each method’s operational constraints.
How Does Butt Welding Work?
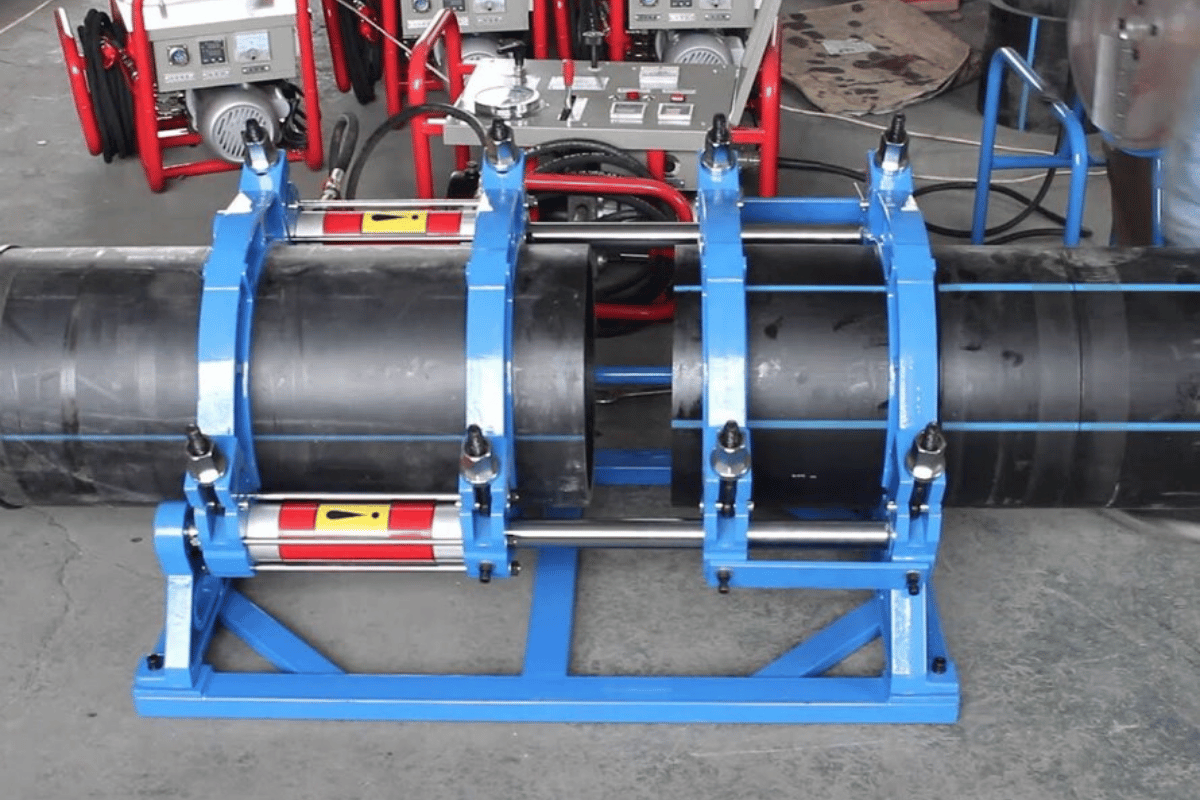
According to standard procedures, butt welding procedures are performed with the help of a specialized butt fusion machine to bring the ends of two pipes ready for welding. The method just begins with a trimmer that will smoothen the ends of the pipe in all fairness. Then, the heater plate warms the pipe ends to a certain degree of moisture, and later, the heater is removed, and the two pipe ends are squeezed optimally. Therefore, when cooled, the melted portion will join together and make a solid and uniform joint. Sufficient break is imperative if any durable weld is to be obtained. This method is reliable, ensuring the attachment comprises no joints as the original pipe.
The Process of Butt Fusion in HDPE Pipes
Butt fusion employed on HDPE pipes is a standard pipe joining method that guarantees a strong and leakproof connection. The procedure has the following steps:
- Pipe Alignment: The pipes are positioned conveniently in the butt fusion machine. This prevents any unnecessary movements and wastage of time during the welding process.
- Facing: A facing device, also known as a trimmer, is used to cut the ends of the pipes and make them smooth and even.
- Heating: The extremities of the superimposed pipes are brought into contact with the heating plate, which is normally regulated to 400 degrees to 450 degrees. This operation ensures that the ends to be joined soften to a specified extent.
- Removal of the Heating Plate: After an appropriate softening, the heater plate is removed, and the ends of the pipe are quickly in contact with each other.
- Fusion and Cooling: The ends of the pipes that have been heated to a molten state are brought into contact with one another using controlled pressure, which is retained until the materials cool to form a permanent homogeneous joint.
One of the technical parameters that are important for succeeding in this process is the temperature of the heater plate, where the state of the material needs to be maintained in a liquid state, and pressure application, which is applied all the time during the heating and cooling stages to make a proper seal. Credible references indeed support these parameters; thus, the operation of the HDPE piping systems becomes accurate and reliable.
Why Butt Welding is Widely Used
Butt welding is one of the techniques primarily employed in the joining of HDPE pipes as it is practical, dependable, and leads to solid connections. Experts and industry sources concur that it is more efficient because it creates a single uninterrupted conduit with less likelihood of leaks than piping using mechanical fittings. Some of the significant reasons for which it is used include:
- Strength and Integrity: This technique is utilized to produce a joint that is stronger than or even equal to the strength of the butt-jointed pipe. It spans the efficiency curve by servicing maintenance needs infrequently and overextending the practical life of the piping system.
- Cost-Effectiveness: To butt weld the mode of juki sew heads, a high one-off cost will be required to purchase equipment and other facilities things including the relevant training; however, butt welding will turn out to be beneficial to many if not all projects considering the reduced financial costs on maintenance and superb leak control in the later days.
- Flexibility and Versatility: Butt welds can be used to connect different thicknesses and diameters of pipes, thereby having a broad range of use in various industries, from gas and water supply to other areas of industrial use.
- Environmental Resilience: The butt-welded pipeline of these HTPE pipes enables and supports systems that are supposed to work in extreme environmental conditions because they don’t rust. HDPE itself is very durable to liquids.
Sealing Head Parameters Certificate
Several bare essentials are critical in ensuring efficient butt welding, for these factors must fall within specific mandated technical parameters:
- Heater Plate Temperature: In this case, the heating plate temperatures should be between 400F and 450F for proper pipe end heating, which is less than the reasonable molten state.
- Pressure Application: Pressure should be uniform during heating and cooling. However, in both cases, Kralik argues that it is difficult to evaluate the applied pressure because parameters such as the diameter and the wall thickness of the pipe dictate it. This means the pressure has to be on the order needed to approximate the two ends of the pipe without actually crushing them.
- Alignment Precision: Last but not least, proper alignment of the butt welding machine is essential to avoid mass concentration in one corner while applying pressure and mass concentration in the other corner for melting during heating, which impacts upon the joined fixturing.
Sticking to these parameters guarantees a comprehensive fusion, which delivers a robust, high-quality, dependable fit for high and adverse exposure conditions.
Tools Required for a Successful Joint
- Butt Fusion Machine: The butt welding procedure also uses the butt fusion machine, which forms the understage of the operation. It comprises a heavy frame that holds and aligns the pipes and one that softens the ends of the pipes before the joining of the pipes.
- Heater Plate: This part operates from 400F to 450F, initiating properly melting the HDPE pipes. Still, regular calibration intervals need to be maintained to ensure the accuracy of the outcomes.
- Trimmer/Planer: This device is perfect for making sure that the pipe ends are uniform so that there will be no defects during the fusion process.
- Alignment Clamps are important for positioning throughout the preparation as they guarantee that pressure during distribution is even and that melting is uniform.
- Pressure Gauge: This is responsible for measuring the pressure subjected during both heat and cool phases, which is necessary to assure a robust union without distorting the pipes.
- Infrared Thermometer: This forecast helped make sure the heater plate temperature was not above or below the temperature level recommended for better fusing.
Through the use of these tools, in combination with a heater plate temperature, application of the pressure, and aligning the workpieces accurately, thermoplastic butt welds of the most demanding quality can be obtained.
What is the Role of Heat Fusion in HDPE Pipe Joining?
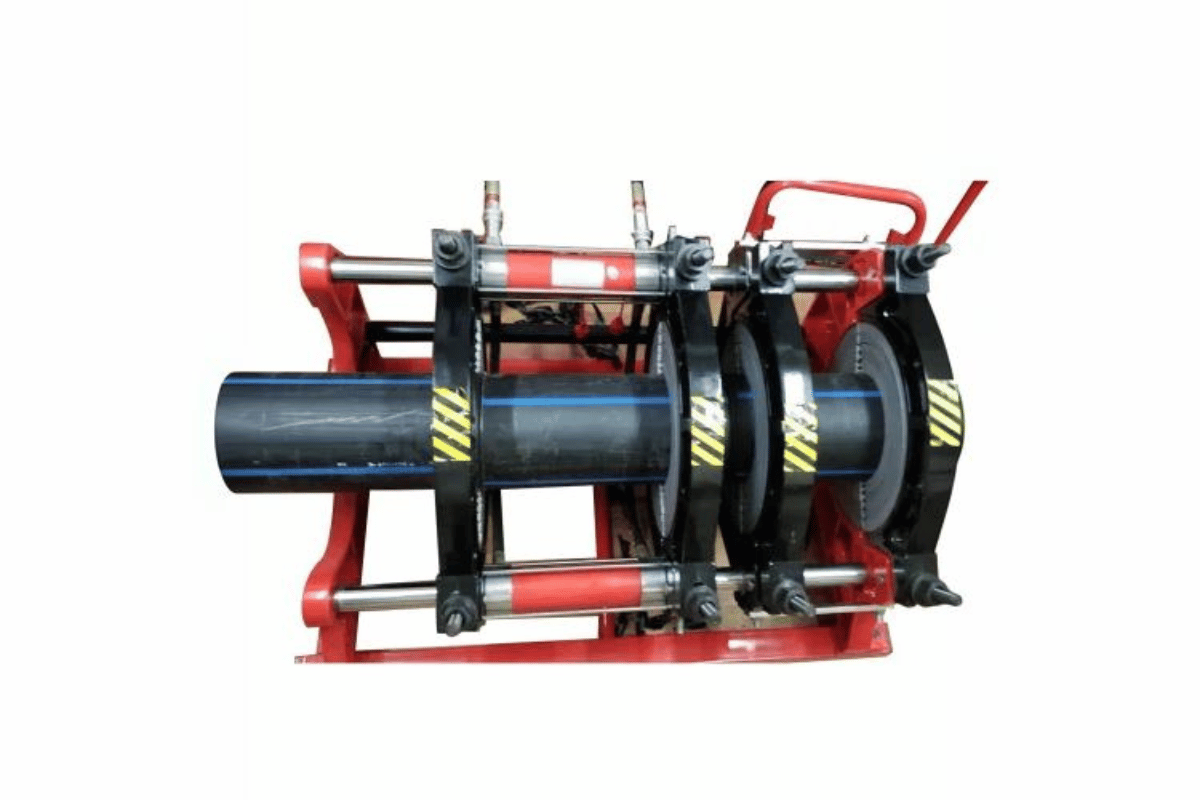

The heat fusion method is critical when joining HDPE pipes since it produces a tamper-proof and unbroken joint between them. The procedure in this regard includes heating the surfaces of HDPE pipes and fitting accessories to bring them to a melting point where they can be joined. This brings about a consistent fabric bond and helps maintain similar strength with the other systems within the piping system. Heat fusion has been largely adopted since it is easy and effective and does not use adhesives or mechanical joints, thus minimizing the weakness and maintenance burden on the system. Due to this ability, the method can be used in several fields and industries where strong and permanent joints are needed.
Explaining Heat Fusion Methods
The methods adopted for joining polyethylene pipes through heat fusion processes include several options employed for specific pipe attributes and project constraints. These include butt fusion, socket fusion, and electrofusion.
- Butt Fusion: Butt fusion joints are mainly used in the joining of large diameter pipes, The ends of the pipes to be fused are placed into the fusion machine to heat each with a contact heater plate and then they are fused lubricated and pressed to form a rigid joint. Basic technology requirements are how well the joints are in alignment, how long it takes to heat the joints, and how long the cooling period is to retain the strength and consistency of the joint.
- Socket Fusion: For small-diameter pipes, the socket fusion process involves heating the pipe and the socket fitting and manually joining the two members. This is done by pushing the hindered pipe into the hot fitting socket. The most important factors are the heating temperature, the time used to introduce the pipe, and the pressure exerted to prevent the formation of defects in the joint.
- Electrofusion: Here, electrofusion couplers are used, which have embedded heating elements known as electrofusion. These elements are heated with an electric current, and the fused pipe surfaces are subjected to pressure, which forms a joint. Some of the pertinent parameters here are the voltage used, heating duration, and cooling duration, which must be managed in order to secure a joint.
The choice of every method depends on the application, cost, and intended life. By following the particular requirements described for each method, durable and high-integrity connections can be achieved, ideal for most demanding applications.
Benefits of Using Heat Fusion in Pipe Systems
Butt fusion, socket fusion, and electrofusion are some of the techniques under heat fusion methods that have fundamental roles in the structural integrity and reliability of pipe systems. These techniques offer several benefits:
- Leakage: Apart from the numerous processes employed in the making of the fittings, heat fusion advantages the use of joints, and thus, its seamless fittings are better than the use of the butt fittings and hence need no gaskets. Consequently, a dependable and efficient piping network is guaranteed for creation.
- Corrosion Proofing: Pipelines attached using socket welding and lap joints better withstand corrosion than metal joints, flanges, and fittings. This considerably improves the system’s life and reliability and cuts down on maintenance and repair costs.
- Versatility: Temperature changes or soil movements do not have to disrupt the performance of heat-fused joints since they are made to withstand such natural events.
- Cost-Effective: The capital expenditure for purchasing the heat fusion tools would be considerably more at the outset; however, the returns from low maintenance and at least partial repairs will be worth the expenditure after years of usage.
Critical factors to the above-outlined methods include the following:
- Butt Fusion: The main required parameters include alignment, correct cooling time after heating, and time needed for heating.
- Socket Joins Fusion: Defects depend on control heating temperature, the correct time for insertion, and pressure on the quality of the product.
- Electrofusion requires precise application of voltage, the duration of the heating element, and management of cooling time to result in a reliable fusion process.
These benefits, combined with specific and accurate parameter controls, make heat fusion technology the best option for constructing strong and effective piping systems for various applications.
Are Compression Fittings a Viable Option?
Compression fittings may be useful in particular situations, especially in cases of emergency and where other methods, such as heat fusion, cannot be applied readily. Such fittings allow ease of mounting and unmounting, making them suitable for temporary or frequent use/maintenance areas. However, compression fittings may not be as secure in leaking against high-pressure and temperature applications as heat fusion. Almost every apparatus depends on the installation’s quality and the environmental conditions in which it operates. Therefore, although applicable in certain situations, compression fittings cannot be considered an alternative to the practical permanent joints commonly attained through heat fusion in most HDPE pipe systems.
Understanding Compression Fittings for HDPE Pipes
As the investigation into the applicability of compression fittings in HDPE pipes continues, it is paramount to comprehend how they work and their use. A compression fitting is a type of mechanical screw fitting that allows for the easy joining of HDPE pipes. They are suited for applications where welding is impractical or when there might be a need to take such fittings apart quickly. This includes elbow compression fittings, bush compression fittings, and so on basic parameters that show the parameters when it comes to fittings and torque, etc. circular, tapering fitters, oft-loading, and unyielding swaged coupling are some of its basic technical parameters.
- Material Composition: These are made from advanced polypropylene plastics or materials, which ensures that they can handle even moderate pressure and external climate.
- Fitting size: The fitting size corresponding to the pipe diameter must be adequate to prevent leaking and ensure proper sealing of the pipe joint.
- Torque Specifications: Applying proper torque does apply here, especially at the time when fittings are being put in so as not to apply less torque, which will mean that leaking will occur due to the joints not being firm or using too much torque and thus destroying either the fitting or the pipe.
Compression fittings offer more flexibility than heat fusion methods but do not provide the same level of performance in terms of durability and leak proofing under highly adverse conditions. The special installation requirements and conditions must be examined in order to select the optimal connection option for the consumer.
Installation Process and Challenges
Simply put, compression fittings for HDPE pipes are installed in stages that ensure proper connections do not leak. First of all, it should be noted that the pipe ends ought to be clean-cut and fitted into the fitting so that they are at a perpendicular angle. The position of the fitting must also be correct so that no excess strain is exerted on the joint. The Main fitting’s nut should be hand tightened first, and the required torque should be applied with a torque wrench, if needed, depending on the size and type of the fittings.
Common Challenges
- Misalignments: Some stresses, when properly aligned, can lead to joint or joint failure. For stress distribution to be uniform when tightening a barb fitting, it is prudent to check if it is aligned before going to the last click.
- Excess or insufficient torquing force: To comply with the manufacturers’ requirements, it is important to use a calibrated torque wrench. Tightening too much can break both the fitting and the pipe, while insufficient tightening can cause leaks.
- Temperature Changes: Temperature variation makes it easy for such pipes to shrink or expand. This should be planned for by fitting some gaps for thermal expansion with an emphasis on the outdoors due to various environments.
Technical Parameters
- Material specification: Materials qualifications should include the ability to hold up against outside environment and provided pressure.
- Torque ratings: For almost all fittings manufactured, manufacturers specify torque limits based on the size and/or type of the fitting; comply to avoid causing leakage or damage.
- Temperature Considerations: Some instructions regarding the economic installation also include locking mechanisms as safety measures, as there are potential dangers related to the structure’s thermal expansion.
By observing these guidelines and preventing these obstacles beforehand, compression fittings can be used with respect to HDPE pipe connections.
Compared with Other HDPE Pipe Joining Methods
However, looking at the various methods of joining HDPE pipes, three methods emerge at the forefront, which include butt fusion, electro fusion, and mechanical joining. Each method has specific advantages and areas of use that logically correspond well with the stated technical parameters.
1. Butt Fusion
- Technical Parameters: This is achieved by applying heat and pressure so that pipe ends are merged into one. Some of these include the heating plate temperature, alignment precision, and cooling time.
- Advantages: It is highly efficient in producing a leak-free, pressure-retaining joint that is tailor-made for the particular pipe line. It is best suited for high-diameter pipes that are to be installed over long durations of time.
- Disadvantages: Some special tools and equipment are needed, and specialized operators are required to do this professional work. It is not practical in all field conditions, especially in space-constrained areas.
2. Electrofusion.
- Technical Parameters: In this case, it employs pullovers with copiously embedded heating elements at the pipe ends to join the two pipe ends. The voltage, current, and time need careful control.
- Advantages: It is possible to link pipes of different diameters and fittings within a limited space. And bonds become solid and homogeneous.
- Disadvantages: The main negative is the high price, which is proportional to the components, which are fittings and equipment. Errors without training are more accessible and, in some cases, are easy to achieve.
3. Mechanical Joining
- Technical Parameters: It entails using mechanical couplings or flanges to hold together the separated pipe ends. Torque and other parameters, as well as material compatibility, are useful factors.
- Advantages: Installation is fast and does not require power or bulky and complex equipment. Bolts come in handy where pool activity needs to transition to or be oriented towards change.
- Disadvantages: There may be leaks due to misalignment or improper torquing. They are generally less reliable for long-term applications than fusion techniques.
Therefore, it is crucial that installers weigh the advantages and prospects of these methods, along with their associated technical parameters, in order to define the best possible piping system requirements in terms of efficiency, durability, and cost.
Why Choose HDPE Pipes for Your Pipe System?
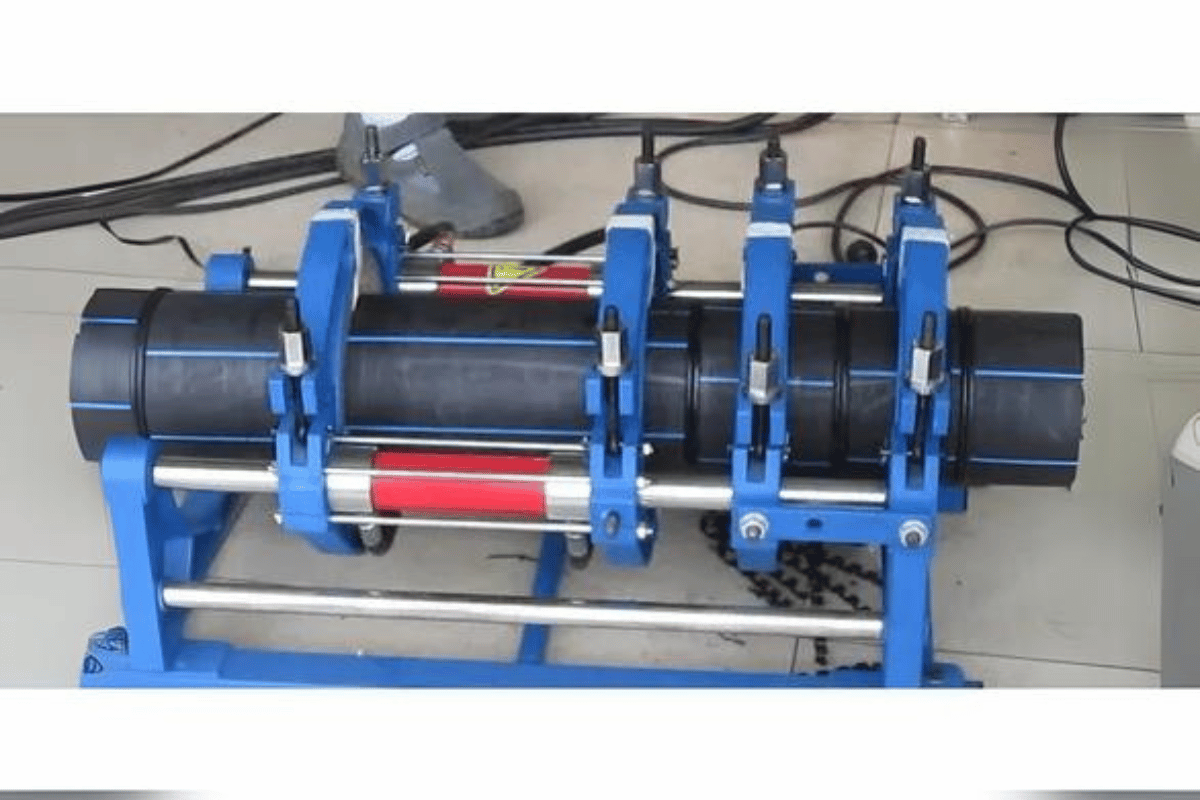
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) piping is becoming the preferred material in modern pipe systems because of its qualities, such as its ease of use and corrosion Euente resistance. The weight of these pipes is low, making them less tedious to move around and fix, hence cutting down on the workforce and energy expended. Synthetic resin plastic pipes such as HDPE are non-metallic, have no biological growth on them, and don’t permit any growth inside the pipes, hence do not allow any blockages or contamination in water pipes. Their flexibility also enables them to adapt to shifting soils, making them ideal for regions susceptible to earthquakes. Furthermore, the potential life span of these pipes during use is about 50 years or more; thus, they are easy and reliable in terms of upfront capital use. As a rule of thumb, comfort, and safety are as crucial as beautification and holistic care. More and more often, solutions sustainable in construction are required in various fields, especially for water supply and drainage, gas, and sewage systems.
Critical Benefits of HDPE Pipe Systems
- Perdurability and Longevity: Among the various features of HDPE pipes is their longevity. They are expected to serve for 50 years plus without any level of abrasion from environmental factors, including extreme sun or temperatures. This lowers the per capita costs and frequency of change or repair.
- Flexibility and Resilience: Constraints in soil movement ooze out IHPE Akathene pipes into seismic areas with less fear of damage when there is a shift in the ground, which leads to leakage or even total breakages.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: HDPE pipes are hygienic, efficient, and non-rusting. They are not corroded by sea water or rust in chemical processes to convey clean water, sewage, and other chemicals and wastes.
- High Flow Capacity: HDPE Pipes have smooth surfaces, which also leads to low resistivity. Less friction ensures faster flow of HDPE Pipes than other pipes, improving system performance and decreasing costs and power savings for pumping.
- Environmentally Friendly: According to life cycle assessments, the making and fitting of HDPE pipes use less energy and emit fewer greenhouse gases than metal pipes. They are also recyclable, therefore reducing wastage.
- Technical Parameters:
- Pressure Rating: HDPE pipes are suitable even under high pressure, as the pressure rating limits range between 100 and 150 psi in most instances.
- Temperature Range: They would be effective from -40°F to 140°F and retain their structure under adverse climate conditions.
These advantages point to the reason why HDPE pipes should be adopted in various fields without compromising on performance, service delivery, or environmental conservation.
Applications of HDPE Pipes in Various Industries
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes upvc pipes have emerged as one of the essential materials in many industries because of their resistance, flexibility, and ecological aspects. Here are some of the most widely used areas:
- Water Supply and Distribution: Thus, the use of HDPE pipes is rampant in water supply systems particularly, mostly because these pipes are not only hard to corrode but also resistant to chemicals and growth matters. Unlike pipes made of concrete and other materials, these systems virtually eliminate the risk of contamination of drinking water, being leak-free for long periods without breakdown.
- Agriculture and Irrigation: Most farmers use HDPE pipes because they are lightweight and do not corrode with fertilizers and pest control products. This enables efficient land irrigation to enhance agricultural sustainability.
- Gas Distribution: The demand for HDPE pipes in the gas distribution system can be attributed to their resistance to high pressure and flexibility. They act as safe means/ routes/ ways of supplying natural gas with minimal maintenance.
- Mining and Industrial Applications: Bulk transportation of slurry, chemicals, and waste has made the use of HDPE pipes more frequent since they are strong and have high flow rates. These transportation means have fewer chances of being corroded or worn out.
- Sewage and Drainage Systems: In sewerage networks, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are used satisfactorily since they do not undergo biodegradation or undergo chemical reactions in those systems, which is a prerequisite if effective waste disposal services are to be guaranteed.
Technical Parameters:
- Pressure Rating: Depending on the application, HDPE pipes may have various pressure rating values, but they are most likely between 100 and 150 psi, which makes them suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Temperature Range: In normal working circumstances, HDPE pipes do not fail within a temperature range of -40°F to 140°F even under tension, and the structure’s integrity remains intact.
These parameters prove that HDPE pipes are preferred whenever we need them, which explains their increasing usage in different industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are HDPE pipes commonly used for?
HDPE pipes are commonly used in various sectors, such as agriculture for irrigation, gas distribution networks, mining, industrial applications, and sewage and drainage systems.
Why choose HDPE pipes over traditional materials?
HDPE pipes are preferred due to their lightweight nature, resistance to chemicals and corrosion, high flexibility, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making them more durable and reliable than traditional materials.
Are HDPE pipes environmentally friendly?
Yes, HDPE pipes are considered environmentally friendly. They are made from recyclable materials and contribute to sustainable practices by reducing leakage and waste due to their durability.
How long do HDPE pipes last?
HDPE pipes are known for their long lifespan, often lasting over 50 years when properly installed and maintained, making them cost-effective.
Can HDPE pipes handle high-pressure applications?
Yes, HDPE pipes are designed to handle high-pressure applications, with ratings typically ranging between 100 and 150 psi. They are suitable for various industrial and distribution systems.





