Large diameter plastic pipe systems play a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from water supply and drainage to industrial processes and infrastructure projects. As the demand for durable, cost-effective, and versatile piping solutions grows, understanding the benefits and considerations associated with these systems becomes increasingly important. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of large diameter plastic pipes, including their types, applications, advantages, and installation considerations. By the end of this guide, readers will have a foundational understanding of how these systems operate and their significance in modern construction and utility management.
What Are Large Diameter Plastic Pipes?

Image source:https://item.taobao.com/
Large diameter plastic pipes are specially engineered piping systems that typically have a diameter exceeding 12 inches. Made from materials such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), HDPE (high-density polyethylene), or PP (polypropylene), these pipes are designed to handle substantial volumes of fluids or gases. They are widely used in various applications including municipal water supply, stormwater management, irrigation systems, and industrial operations. The lightweight nature of plastic, combined with its resistance to corrosion and ease of installation, makes large diameter plastic pipes an attractive alternative to traditional materials like metal or concrete in construction and utility projects.
Understanding the Basics of Large Diameter Pipe Systems
In my exploration of large diameter pipe systems, I’ve come to understand that these systems are crucial for efficiently transporting fluids over long distances. Generally, they are designed to withstand high pressure and flow rates while minimizing the risk of leaks. The materials used, such as PVC, HDPE, and PP, provide excellent durability and resistance to various environmental factors. Furthermore, I found that installation methods can vary based on the specific application and site conditions, but their lightweight nature simplifies handling. Ultimately, large diameter plastic pipes play a significant role in enhancing the reliability and effectiveness of modern infrastructure projects.
Comparing Large Diameter HDPE Pipe and PVC Pipe
In my analysis of large diameter HDPE (high-density polyethylene) pipe versus PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipe, I quickly recognized several distinct characteristics that influence their applications and performance. For starters, HDPE tends to have a higher resistance to impact and is more flexible, which allows it to adapt better to ground movements or shifts. This flexibility is evident in HDPE’s ability to withstand pressures of up to 160 psi, making it suitable for high-pressure applications like gas distribution and water transmission in dynamic environments. Conversely, PVC pipes typically have a lower pressure rating, around 100 psi, but they are generally more rigid, making them ideal for applications where structural integrity is paramount.
From an installation perspective, both materials offer advantages—HDPE’s lightweight nature simplifies transport and reduces installation costs, while PVC’s durability and resistance to corrosion make it reliable for long-term use. Additionally, I noted that HDPE provides superior resistance to a wider range of chemicals compared to PVC, allowing it to be used in more diverse applications. On a cost basis, HDPE pipes tend to be more expensive initially, but their longevity and lower maintenance needs can lead to cost savings over time. Therefore, the choice between large diameter HDPE and PVC pipes depends largely on the specific requirements of the project, including environmental conditions, pressure ratings, and budget constraints.
Common Applications for Large Diameter Pipes
Large diameter pipes are commonly used in various industries due to their ability to handle substantial volumes of fluids while maintaining structural integrity. Here are some key applications, with corresponding technical parameters:
- Water Transmission: Large diameter HDPE and PVC pipes are frequently employed in municipal water supply systems. Typically, HDPE pipes are used for pressures up to 160 psi, while PVC pipes operate safely at around 100 psi. The choice often depends on the flexibility required for the installation conditions and the chemical composition of the transported water.
- Sewage and Wastewater Management: In sewage systems, large diameter pipes facilitate the efficient transport of wastewater. HDPE’s resistance to corrosive materials makes it preferable for applications where chemical exposure and ground movement are concerns. Standard sizes range from 12 inches to over 60 inches in diameter.
- Stormwater Drainage: Large diameter pipes are essential in managing stormwater runoff. The material’s durability and flexibility allow them to withstand environmental pressures, with HDPE handling varying installation environments and PVC providing long-lasting structural integrity.
- Industrial Applications: Various industries including oil and gas, mining, and chemical processing rely on large diameter pipes to transport raw materials and byproducts. HDPE’s higher chemical resistance allows it to dominate in harsh environments, while PVC can be advantageous when focusing on cost efficiency and lower temperature applications.
- Irrigation Systems: Agriculture often requires significant water transport, where large diameter pipes improve irrigation efficiency. Their design must consider flow rate requirements, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM), with HDPE managing higher flows due to reduced friction losses compared to PVC.
The selection of large diameter pipes must take into account these applications and their specific technical requirements, including pressure ratings, flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Each application will dictate which characteristics are most critical to ensure successful implementation and operation.
How Are Large Diameter Pipes Installed?
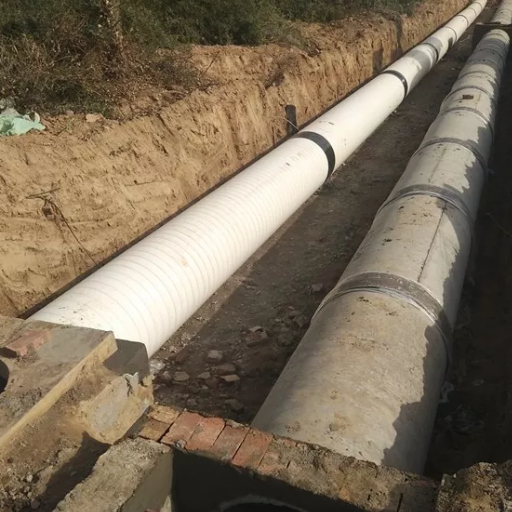

The installation of large diameter pipes involves several key steps to ensure proper alignment and secure connections. Initially, a site assessment is conducted to evaluate soil conditions, necessary excavation, and environmental factors. Following this, trenching or boring is performed to create the appropriate path for the pipes while adhering to regulatory guidelines. Once the trench is prepared, the pipes are laid out and connected using appropriate joining methods, such as welding for HDPE or solvent cement for PVC. Finally, the installation is completed by backfilling the trench to compact the soil around the pipes, ensuring stability and protection against external pressures. Proper testing, such as leak detection and pressure tests, is also carried out before the system is put into operation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Pipe Installation
As I researched the top resources on pipe installation, I compiled the following concise steps along with key technical parameters. This guide reflects common practices and ensures a thorough installation process:
- Site Assessment: I begin by evaluating the site conditions, including soil type, water table level, and possible environmental impacts. This allows me to anticipate challenges and plan the installation accordingly.
- Trenching: Next, I prepare the trench according to regulatory specifications. The depth and width should adhere to the pipe diameter and the anticipated load. For large diameter pipes, a common trench width is at least twice the diameter of the pipe to accommodate proper installation.
- Pipe Preparation: Before laying the pipes, I inspect them for any damage and ensure that they meet the specified pressure ratings. For instance, HDPE pipes are often rated for high pressure, while PVC typically handles lower pressure applications.
- Laying the Pipes: I align the pipes according to the planned layout, ensuring they are spaced appropriately to avoid stress and allow for any necessary expansion. The recommended spacing often depends on the pipe diameter and material used.
- Joining Methods: According to specifications, I employ correct joining techniques. For HDPE, fusion welding is standard, while for PVC, I use solvent cement. The joint integrity is crucial for preventing leaks, so I ensure that the methods adhere to manufacturer guidelines.
- Backfilling and Compaction: After connecting the pipes, I backfill the trench with suitable materials. I avoid sharp rocks and debris that could damage the pipes. Compaction should be done in layers to provide uniform support and prevent settling.
- Testing: Finally, I conduct pressure tests and leak detection measures to ensure the system’s integrity before it becomes operational. This typically involves filling the system with water and monitoring for pressure drops, which can indicate leaks.
Following these steps, with careful consideration of technical parameters such as pipe material, pressure ratings, and installation technique, ensures that large diameter pipe systems are installed effectively and reliably.
Essential Tools and Fittings for Installation
To successfully install large diameter pipe systems, several essential tools and fittings are necessary. Key tools include a pipe cutter for precise cuts, a fusion welding machine for HDPE pipes, and a solvent cement applicator for PVC. Additionally, a trenching machine may be required for excavation, alongside standard tools like shovels, rakes, and compaction equipment for backfilling. Regarding fittings, ensure you have an assortment of couplings, elbows, and flanges that match your pipe material and diameter, as these components are vital for creating secure and reliable connections throughout the system. Having the right tools and fittings on hand not only streamlines the installation process but also enhances the overall quality of the project.
Common Challenges in Installing Large Diameter Pipe
Installing large diameter pipes does come with its set of challenges that can impact the overall success of a project. Some of the most common issues include:
- Site Access and Space Constraints: Often, job sites are limited in space, making it difficult to maneuver heavy equipment and materials. This can delay the installation process, especially in urban environments where space is at a premium.
- Soil Conditions: The type of soil can significantly affect the installation process. For example, loose soils may require additional excavation and stabilization efforts. Understanding the soil composition is critical, and technical parameters such as soil bearing capacity should be assessed to prevent future issues.
- Alignment and Grade Control: Maintaining proper alignment and grade is crucial to ensure the system functions effectively. Deviations can lead to increased pressure on joints and potential failures. Utilising laser levels and grade stakes can assist in achieving accurate placement.
- Hydraulic Design Considerations: Large diameter pipes must be designed to manage flow rates and pressures effectively. Technical parameters such as flow velocity, friction loss, and water hammer must be carefully considered to prevent hydraulic issues post-installation.
- Weather Conditions: Extreme weather can pose challenges during installation, from heavy rains that may lead to flooding in trenches to freezing temperatures impacting material integrity. It’s essential to monitor forecasts and plan accordingly to mitigate these environmental risks.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, along with a focus on pertinent technical parameters, the efficiency and reliability of large diameter pipe installations can be significantly enhanced.
What Are the Benefits of Using Large Diameter Pipes?

Using large diameter pipes offers several key benefits, particularly in the context of fluid transport and drainage systems. First, they facilitate a higher flow capacity, enabling efficient movement of water and other fluids, which is essential in urban infrastructure and industrial applications. Second, the larger diameter reduces the velocity of the fluid, minimizing the risk of erosion within the pipe and decreasing wear over time. Third, these pipes can accommodate fluctuations in flow, which is crucial during peak demand periods or heavy rainfall events. Additionally, large diameter pipes often require fewer joints and fittings, which can lead to reduced maintenance and installation costs. Overall, the robustness and efficiency of large diameter pipes make them a reliable choice for diverse engineering needs.
Advantages of Large Diameter HDPE Pipes
In my experience, large diameter HDPE pipes offer several significant advantages that make them a preferred choice for many applications. Firstly, their lightweight nature simplifies transportation and installation, reducing overall project timelines and labor costs. Additionally, HDPE pipes are resistant to corrosion and chemical reactions, which ensures durability and longevity even in harsh environments. The flexibility of HDPE allows for easier handling and installation in challenging terrains. Furthermore, their smooth interior surface minimizes friction loss, enhancing flow efficiency. Overall, these advantages combined contribute to lower lifetime costs, making large diameter HDPE pipes an ideal solution for fluid transport systems.
Long-term Performance and Durability
The long-term performance and durability of large diameter HDPE pipes are primarily attributed to their material properties and design features. HDPE pipes can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -40°F to 140°F (-40°C to 60°C), making them suitable for various environmental conditions. Additionally, their resistance to environmental stress cracking (ESC) allows for a service life of over 50 years when properly installed and maintained.
Key Technical Parameters:
- Density: HDPE has a density of around 0.95 g/cm³, contributing to its lightweight characteristics.
- Flexural Modulus: Typically around 1,000-1,200 MPa, indicating good flexibility and impact resistance.
- Working Pressure Rating: HDPE pipes can handle pressures ranging from 100 to 200 psi, depending on wall thickness and diameter.
- Temperature Resistance: Effective in applications with a temperature range of -40°F to 140°F (-40°C to 60°C).
These parameters underline the ability of large diameter HDPE pipes to maintain their structural integrity and operational efficiency throughout their lifecycle, thus ensuring reliability in fluid transport systems even under demanding conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Large diameter HDPE pipes offer significant cost-effectiveness and efficiency in fluid transport systems. The lightweight nature of HDPE reduces transportation and installation costs, as less manpower and equipment are needed compared to traditional materials. Furthermore, the corrosion resistance of HDPE minimizes maintenance and replacement costs over time, adding to its long-term financial benefits. The pipes’ capacity for high flow rates reduces energy consumption in pumping systems, enhancing overall operational efficiency. Consequently, the combination of lower initial investment and reduced lifetime costs positions large diameter HDPE pipes as a financially savvy choice for various fluid transport applications.
Technical Specifications of Large Diameter Pipes

When evaluating large diameter pipes, several key specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. These include:
- Diameter: Large diameter pipes typically range from 6 inches to 63 inches or more, allowing for substantial fluid capacity.
- Material Standard: Compliant with industry standards such as ASTM, AWWA, or ISO, ensuring reliability and compatibility for various environments.
- Joinery Method: Options include heat fusion, mechanical joints, and electrofusion, each providing distinct benefits in terms of strength and ease of installation.
- Hydraulic Characteristics: Critical for determining flow capacity and efficiency, including roughness coefficients and flow velocity limits.
- Environmental Resistance: Evaluating resistance to chemicals, UV exposure, and temperature variations is crucial for longevity and performance.
These specifications play a pivotal role in assessing the suitability of large diameter pipes for diverse applications in various industries.
Understanding Nominal Diameter and Outside Diameter
In piping systems, distinguishing between nominal diameter (ND) and outside diameter (OD) is vital for ensuring compatibility and performance.
- Nominal Diameter (ND): This is a standardized designation used to describe the internal diameter or the approximate size of the pipe. It does not correspond directly to any actual measurement and serves primarily as a reference for fitting and components. For example, a pipe with a nominal diameter of 8 inches may have an actual internal diameter that varies depending on the material and wall thickness.
- Outside Diameter (OD): The outside diameter refers to the total external measurement of the pipe. This dimension is crucial for space management, installation, and interfacing with other systems. For example, a pipe classified as 8 inches nominal diameter may have an OD of 8.625 inches if it is a schedule 40 steel pipe.
Understanding these parameters helps in determining the appropriate pipe size for existing fittings, valves, and other components, thereby preventing compatibility issues. Here are some corresponding technical parameters to consider:
- Wall Thickness: This impacts both the ND and OD, influencing the pipe’s strength and pressure ratings.
- Weight per Unit Length: This plays a role in understanding the handling and installation requirements.
- Pressure Rating: Knowing the pressure classes applicable to the given OD ensures safe operation within intended applications.
By comprehending both nominal and outside diameters alongside these technical parameters, engineers and practitioners can make informed decisions in selecting the right large diameter pipes for their specific transport applications.
Material Ratings and Resistance
When selecting large diameter pipes, it’s essential to understand the material ratings and resistance levels to ensure they meet specific application requirements. Different materials, such as PVC, steel, and fiberglass, have varied ratings based on their chemical resistance and the environmental conditions they are expected to endure. For instance, steel pipes are known for their high strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications, whereas PVC pipes excel in areas requiring corrosion resistance.
Each material is also rated for its ability to handle temperature changes and exposure to specific chemicals, influencing their longevity and performance. Understanding the material’s stress rating, temperature rating, and chemical compatibility is crucial in choosing the right pipe for any application. Additionally, practitioners should consider the environmental factors, like weather and soil conditions, which can impact the material’s resistance over time. Thus, thorough evaluation of material ratings is key to ensuring safe and efficient operation of piping systems.
Industry Standards and Technical Requirements
In my experience, adhering to industry standards and technical requirements is vital when selecting large diameter pipes. These standards, often defined by organizations such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and AWWA (American Water Works Association), provide crucial guidelines on material performance, installation protocols, and testing methods. For example, pipes must meet specific specifications regarding pressure ratings, structural integrity, and corrosion resistance, which are outlined in these standards. By ensuring compliance with these established norms, I can guarantee that the chosen piping systems not only meet regulatory requirements but also perform reliably in their intended applications. Additionally, staying informed about updates to these standards helps me make better decisions that align with current best practices in the industry.
How to Choose the Right Pipe and Fittings

Selecting the appropriate pipe and fittings involves several key considerations. First, assess the specific application requirements, including the type of fluid being conveyed, pressure, and temperature conditions. Next, consider the material options available, such as PVC, CPVC, steel, or copper, each offering unique benefits and limitations regarding durability and corrosion resistance. Evaluate the necessary fittings for proper connections, ensuring they match the pipe’s diameter and material. Furthermore, take into account local codes and regulations to ensure compliance. Lastly, consult industry standards for guidance on performance criteria and installation practices, as these will help ensure longevity and reliability in your piping system.
Factors to Consider in Pipe Selection
When selecting pipes, several critical factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity:
- Material Compatibility: Choose a material that is compatible with the fluid being transported. For example, PVC is suitable for water, while steel is better for high-pressure applications.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Ensure that the pipe can handle the specific pressure and temperature conditions of the application. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid potential failures.
- Corrosion Resistance: Consider environmental factors that may lead to corrosion. Materials such as stainless steel or certain plastics may offer better resistance in harsh conditions.
- Diameter and Flow Requirements: The diameter of the pipe should be appropriate for the flow rate needed in the system. A larger diameter may be required for higher flow rates to minimize pressure drops.
- Installation Environment: Assess the installation location for any factors that may affect pipe integrity, including exposure to chemicals, temperature fluctuations, or physical stress.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed choice that aligns with both the technical requirements and the regulatory standards applicable to your project.
Matching Fittings with Pipes
When matching fittings with pipes, it’s essential to ensure compatibility in terms of size, material, and pressure ratings. First, select fittings that match the diameter of your chosen pipe to maintain proper flow and prevent leaks. Additionally, consider the material of the fittings; using fittings made from the same material as the pipes, such as PVC or metal, enhances durability and reduces the risk of corrosion at the connection points. Lastly, verify that the fittings have appropriate pressure ratings that align with the intended application, ensuring a secure and reliable connection within the piping system.
Working with Engineers and Manufacturers
Collaborating effectively with engineers and manufacturers is crucial for the successful execution of any piping project. First, establish clear communication to define project specifications, timelines, and potential challenges. Involving engineers from the outset allows for technical considerations to be integrated early, ensuring that all systems are designed optimally. It’s also essential to work with reputable manufacturers who can provide high-quality materials and fittings that meet industry standards. Requesting samples and conducting quality checks can help maintain the integrity of the project. Additionally, consider involving engineers during the manufacturing process to address any design changes or adaptations that may arise, fostering a collaborative approach to problem-solving.
Customer Service and Support for Large Diameter Pipes
Customer service and support are vital components in managing large diameter piping projects, as they contribute to seamless operations and customer satisfaction. Providing dedicated support teams who are knowledgeable about large diameter pipes ensures that clients can receive prompt assistance with inquiries, installation guidance, and troubleshooting. Additionally, offering comprehensive training on proper handling and usage of these larger fittings can enhance user confidence and reduce mistakes. It’s also beneficial to establish a clear protocol for addressing warranty claims and service issues, ensuring that any defects or concerns are resolved efficiently. This proactive approach not only enhances the customer experience but also builds trust and long-term relationships with clients.
Finding Reliable Customer Service Providers
When seeking reliable customer service providers for large diameter pipes, consider the following criteria to ensure exceptional support and service:
- Industry Experience: Look for providers with a proven track record in the piping industry, particularly in handling large diameter projects. Their experience can reflect their ability to understand complex issues that may arise.
- Technical Expertise: Ensure the provider employs personnel with technical backgrounds in engineering or relevant fields. This expertise is crucial for offering sound advice on installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
- Availability of Support: A reliable customer service provider should offer multiple channels of communication, such as phone, email, and live chat, with support available during extended hours to assist clients promptly.
- Response Time: Evaluate the average response time to inquiries and service requests. A commitment to rapid response indicates a provider prioritizing customer needs.
- Training Programs: Providers that offer comprehensive training programs empower users with knowledge about handling large diameter pipes. This should include sessions on safety, installation techniques, and maintenance best practices.
- Warranty and Service Policy: Review the warranty terms and service policies. Reliable providers should have clear procedures for warranty claims, defect resolutions, and after-sales support.
- Client Testimonials and References: Seek feedback from existing customers regarding their experiences. Positive testimonials can indicate reliability and the level of service provided by the company.
These considerations will help ensure that the chosen customer service provider can effectively meet the technical and operational needs of projects involving large diameter pipes.
Technical Support and Engineer Assistance
To ensure effective technical support and engineer assistance, it is essential to have a dedicated team that not only understands the intricacies of large diameter pipes but also provides timely and practical solutions. This team should be equipped to address various challenges, from installation queries to maintenance concerns. Effective channels for communication are vital, allowing clients to reach out with questions or issues promptly. Additionally, a responsive support system will enhance client confidence, ensuring they receive the necessary guidance when needed. By prioritizing accessibility and expertise, companies can foster a strong support framework that addresses client needs efficiently.
Handling Shipping and Delivery Concerns
Addressing shipping and delivery concerns is critical to maintaining a smooth workflow for projects involving large diameter pipes. Below are key considerations and associated technical parameters:
- Shipping Methods: It’s essential to evaluate various shipping options such as standard freight, expedited shipping, and flatbed transport. Each method varies in cost, delivery time, and suitability depending on the size and weight of the pipes.
- Logistics Coordination: Collaborate with logistics providers who specialize in heavy or oversized loads. This ensures compliance with local regulations and safe transport. Key parameters include weight limits, route restrictions, and necessary permits.
- Delivery Timelines: Clearly defined timelines for delivery are crucial. Establish realistic timelines that account for production schedules, shipping methods, and potential delays caused by weather or logistical challenges.
- Tracking Systems: Implement tracking solutions that allow clients to monitor shipment status in real-time. This enhances transparency and helps manage expectations regarding delivery.
- Packaging Standards: Proper packaging techniques must be utilized to protect pipes during transit. This includes using braces, edge protectors, and moisture barriers tailored to the size and material of the pipes.
By addressing these shipping and delivery aspects with corresponding technical parameters, companies can significantly minimize disruptions and enhance client satisfaction throughout the project lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the largest diameter PVC pipe available?
A: The largest diameter PVC pipe available can reach sizes up to 80 inches. These pipes are commonly used for large-scale applications like wastewater treatment plants and gravity pipelines.
Q: What are the benefits of using large diameter PVC pipes?
A: Large diameter PVC pipes offer benefits such as durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. They are also available in sizes that can meet a variety of applications, from residential to industrial use.
Q: How does ISCO contribute to large diameter pipe solutions?
A: ISCO provides comprehensive pipe products and services, including the fabrication of large diameter PVC pipes and HDPE large diameter pipes. They deliver innovative solutions for various applications, ensuring high-quality and reliable pipeline installations.
Q: What is DWV and how is it used in large diameter pipes?
A: DWV stands for Drain, Waste, and Vent. It refers to a system of pipes that remove wastewater and prevent sewer gases from entering buildings. Large diameter DWV pipes are crucial for efficient wastewater management in large-scale projects.
Q: Can large diameter PVC pipes be used for offshore projects?
A: Yes, large diameter PVC pipes are suitable for offshore projects. They are often used in offshore pipelines due to their resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Q: What does the term “fuse” mean in the context of large diameter pipes?
A: “Fuse” refers to the process of joining pipes together using heat to melt and fuse the pipe ends. This method is commonly used with HDPE large diameter pipes to create a strong, leak-proof joint.
Q: What sizes are available for large diameter HDPE pipes?
A: Large diameter HDPE pipes are available in sizes ranging from 100 mm to 3,500 mm. These pipes are used for a variety of applications including water supply, drainage, and sewage systems.
Q: What is the significance of the largest solid wall HDPE outfall in North America?
A: The largest solid wall HDPE outfall in North America represents a significant achievement in pipeline technology and engineering. It showcases the capability to fabricate and install large-diameter pipelines for extensive and demanding applications.
Q: How does horizontal directional drilling benefit the installation of large diameter pipes?
A: Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) allows for the installation of large diameter pipes with minimal surface disruption. This technology is especially useful in urban areas or environmentally sensitive regions, reducing the impact on existing infrastructure and ecosystems.
Q: What innovative applications are available for large diameter PVC pipes?
A: Large diameter PVC pipes are used in a variety of innovative applications such as point wastewater treatment plants, offshore pipelines, and gravity sewer systems. Their versatility and unmatched durability make them suitable for new applications in both residential and industrial settings.





