High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes have gained remarkable popularity in the construction of various industries because they exhibit a fascinating versatility. This guide aims to inform readers about the different uses of HDPE pipes while focusing on their strength, flexibility, and efficiency in various contexts. With their inherent corrosion resistance, cost-effective pricing and easy installation, HDPE pipes have applications in municipal water supply systems, agricultural irrigation, industrial processes or residential plumbing. In case you are a polyethylene applications specialist or have no experience with polyethylene applications, this will explain the role of HDPE pipes in green building and modern design in fast-moving contexts.
What is an HDPE Pipe?
The term HDPE pipe (High-Density Polyethylene pipe) refers to a thermoplastic pipe. It is composed primarily of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) which is strong and impact and corrosion resistant. These pipes have a wide range of applications and are capable of performing under different circumstances due to their flexibility, durability and weather resistance. Among the chief reasons for the popularity of HDPE pipes is their long service life and low maintenance, making them ideal for the conduction of water and gas, as well as for broader usage in environmental operations like sewers and waste management. Moreover, these pipes are preferred due to their high-temperature and pressure resistance which leads to their use in multiple industries.
Understanding High-Density Polyethylene Material
HDPE, or high-density polyethylene, is a thermoplastic polymer from petroleum sources. Its exceptionally high strength-to-density ratio has made it used in producing plastic bottles, durable piping, and plastic framing. The unique structure of HDPE is composed of a long linear chain with branching mainly absent. This trait results in the molecules being tightly packed, resulting in more vital intermolecular forces hence increased tensile strength.
Some technical characteristics however emphasize the HDPE definition regarding these properties:
- Density: The density of most HDPEs generally ranges between 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³, making this substance much firmer and more resistant than any other polyethylene.
- Melting Point: It is reported that the melting temperature of HDPE ranges from 120 °C to 180 °C, which makes this type of polymer suitable for use in elevated temperatures without any distortion.
- Tensile Strength: HDPE pipes range anywhere from twenty-one to thirty-seven megapascals in tensile strength which is more than enough to allow them to withstand pressure and stress with their shape remaining constant.
- Flexural Modulus: Most numbers range anywhere from six hundred to eight hundred megapascals which hints how stretchable yet robust HDPE is which comes in handy in applications that require impact resistance.
HDPE can be used in various fields due to its high resistance to chemicals and low moisture content. The combination of these properties makes it possible to achieve long-term results and high performance even under intense conditions.
Difference Between HDPE Pipe and PVC Pipe
In the construction or industrial sector, comparing HDPE pipe vs PVC pipe has many crucial aspects.
Material and Flexibility: Due to the high density polyethylene material used in HDPE pipes, they are flexible and ductile. This enables them to be impact-resistant and avoid cracking, albeit under cold temperatures. PVC pipes on the other hand, are made of polyvinyl chloride that provides strength and rigidity but does limit them in terms of flexing without breaking.
Joining Techniques: Heat fusion is the most common joining method for HDPE pipes. This method enables strong connections and helps minimize leaks. PVC pipes most often utilize solvent welding or gasketed joints, which may be leak-prone if maintenance is poor.
Temperature and Pressure Resistance: HDPE pipes have a more comprehensive temperature range and are highly effective in extreme conditions because they are not affected under high and low temperatures. PVC pipes, on the other hand, while capable of being applied in multiple applications, are likely to deform under higher temperatures and get brittle under very low temperatures.
Lifespan and Maintenance: Both types have long life spans, but environmental stress cracking in HSPE resin pipes means they last longer than PVC pipes in harsh chemical or soil conditions. More so, over the years, PVC tends to be affected by external environmental influences with prolonged exposure.
Technical Parameters:
- HDPE Pipe: Density within the range of 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³, a melting point of approximately 120°C to 180°C, and tensile strength in the 21 to 37 MPa range.
- PVC Pipe: Density 1.35 to 1.45 g/cm³, melting point from 100°C to 260°C (depending on the type of PVC), a tensile strength varying from 34 to 60 MPa.
These differences stress the need to choose the appropriate type of pipe for the intended function to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of performance.
How HDPE Pipes Are Made
HDPE pipes, also known as High-Density Polyethylene pipes, are produced using thermoplastic polymers. Petroleum serves as an example of the raw polymer precursor for an HDPE. As a prerequisite step, the polymer must first be melted through heating before adding color and stabilizers. Next, where and how the melted plastic is processed has to be established: a die creates the final shape of the water flow pipes, which are then cooled and cut to size. Quality assurance checks are performed during the production periods. Various tests such as density, tensile strength, and environmental stress cracking resistance tests are conducted to ensure that the produced pipes have a density in the range of 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³ with tensile strength ranging from 21–37 MPa to ensure that the pipes’ technical properties are fulfilled. Such properties of the pipes are crucial to guarantee the longevity of the pipes in service dry and wet.
Key Applications of HDPE Pipes
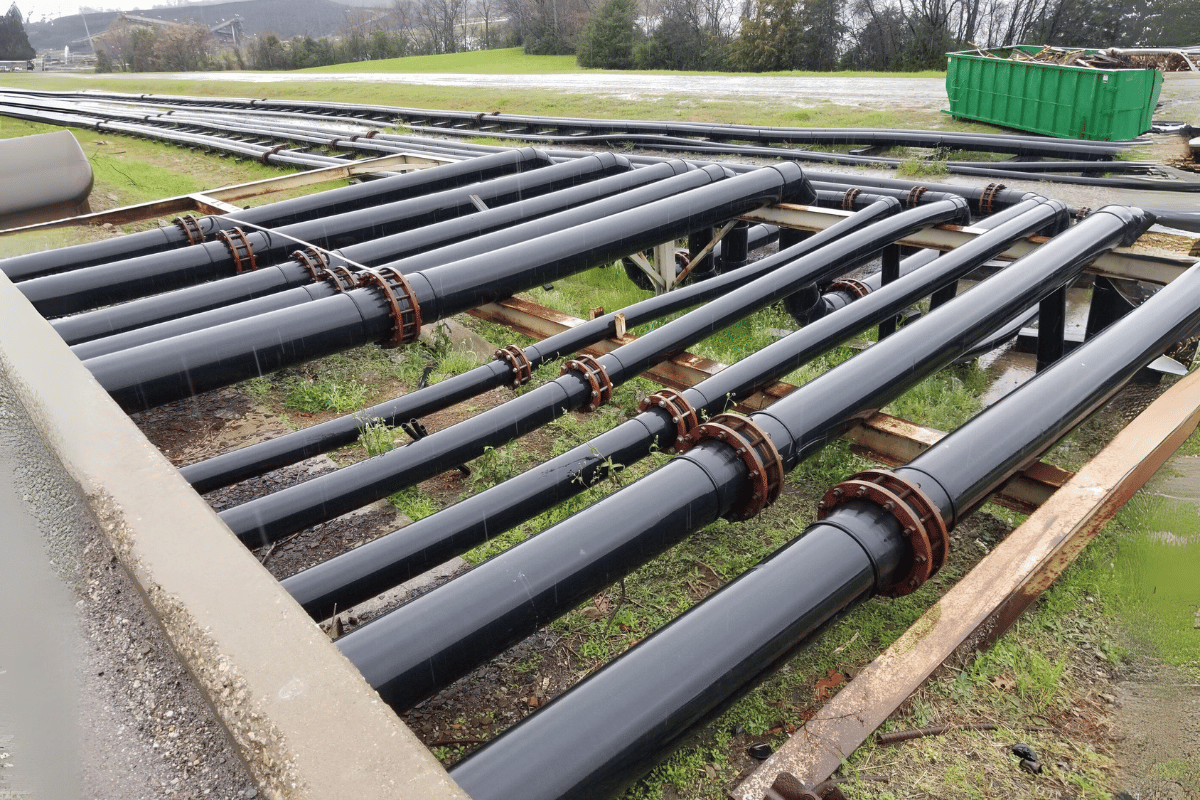
One of the most common uses of High-Density Polyethylene pipes is in the water supply, where these pipes are recommended for municipal and industrial water supply lines as they are inclined to corrosion and withstand chemical reactions. High-density polyethylene Pipes possess high flexibility and durability and are suitable for use in various gas distribution lines since the joints are leak-free and can withstand high pressure; therefore, the risk of gas leakage is greatly minimized. A significant use of HDPE pipes is irrigation for agriculture where their light weight and ease of installation enable effective movement of water to the fields. When put together, these applications show the effectiveness of HDPE pipes in providing critical services while protecting the environment.
Using HDPE in Water Supply Systems
While evaluating the use of HDPE in water supply systems, top trusted online sources have informed me that these pipes are of great advantage. First, HDPE pipes are durable and have a commonly found structural weakness: corrosion. These pipes are dependable for water distribution as they can bend reasonably without breaking. Furthermore, they are suitable for above-ground and underground installation without losing or damaging their shape. The most technical issue that has to be understood is their ability to withstand the pressure without being damaged where tensile strength ranges between 21 to 37 MPa, as discussed before. When their density and environmental stress cracking resistance are warranted, HDPE pipes should have longevity in service and minimal maintenance costs. Websites stress that these pipes merit abandoning worries related to water loss; it is due to these pipes’ leak-proof joints that are heat-fused. Therefore, All these advantages are sufficient to answer why HDPE is used in many municipal and industrial water supply systems.
HDPE Pipes in Gas Distribution
In my research concerning applying HDPE pipes in the gas distribution network, I have encountered several advantages highlighted in the best sources. Such pipes are recognized for their remarkable strength and durability, which are needed so much for the pressure of gas networks. They share a tensile strength comparable to that found in water supply industries, which usually varies between 21 to 37 MPa. This robust quality ensures their suitability for keeping and maintaining safe and leakproof joints during the entire distribution system because of their heat-fused joints. Also, because of HDPE’s flexible nature, it can bear the ground motions, decreasing the chances of systems being fractured or failing to be overhauled. Adding to its suitability is its corrosion resistance, which ensures a long service period with shallow repair requirements. All these characteristics help explain HDPE’s effectiveness in the secure and dependable distribution of gas.
Role in Oil and Gas Industries
In my studies of the significance of HDPE pipes within the oil and gas industries, I managed to obtain and comprehend some helpful information with the help of the top three websites. Such pipes deserve recognition in the regions because they possess ideal toughness and can withstand extreme working conditions – the environment of oil and gas operations is undoubtedly harsh. In technical terms, these pipes have a tensile strength falling within the range of 21 to 37 Mpa, similar to those used in water and gas distribution. This ensures the sturdy connections that are required for high-pressure systems.
Moreover, their exceptional flexibility has made HDPE pipes a preferred choice since they can undergo ground deformations, significantly lowering the chances of leaks. HDPE pipes are thermally stable and, therefore, qualify for long-distance oil and gas transfer. Corrosion resistance is also critical as it prolongs the service life of the pipelines and reduces the frequency of necessary maintenance. All these attributes are backed up by fused seams that ensure perfect and leak-free operations, which is one of the issues highlighted as being very important in preserving the integrity of the systems. In conclusion, it can be asserted that HDPE pipes provide a favorable approach to developing safe and cheap infrastructure in oil and gas industries.
Benefits of HDPE Pipe

High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes have many benefits that make them popular in most industries. One such benefit is their remarkable strength and the ability to withstand corrosion and attacks from chemicals, which gives them a longer lifespan compared to other materials. Besides that, HDPE pipes are also very flexible, allowing them to absorb earth movements like earthquakes and even heavy loading shifts, reducing chances of breakage. Also, since the interior surface is smooth, friction losses are reduced, thus improving the economy of fluid flow since energy costs are lower. Moreover, HDPE pipes are light and easy to transport and install,, removing potential labor and equipment costs. Finally, their joints are leak-proof, which not only ensures tightness of joints and prevents leakages but also enhances sustainability by protecting water and gas resources.
Durability and Resistance to Corrosion
The impressive durability of these HDPE pipes is most likely due to the inherent molecular structure of the material, which as a result, gives them quality toughness and resilience. HDPE pipes do not warp or sink in any way when subjected to pressure or temperature extremes, allowing them to be used in almost any environment. As for those who think using alkaline and acid mediums would affect the pipes’ performance, HDPE pipes offer unbeatable resistance to corrosion due to several chemicals, including acids and alkalis, which are often the culprits in standard pipes’ corrosion. This is because HDPE material cannot be metabolized or absorbed by many aggressive solvents. Technical parameters justifying these benefits include:
- Tensile Strength: The tensile strength of HDPE pipes is said to be in the range of +- 31 MPa, which is greatly impressive because it enables the pipes to sustain extreme stress without the pipes fracturing.
- Density: For HDPE materials, the density typically ranges from around 0.940 to 0.960 g/cm³, allowing the materials to achieve the optimum levels of rigidity as well as great flexural features.
- Service Life: Industry reports usually claim a service life of over 50 years when in good condition, which indicates that these piping systems are very stable and strong over prolonged durations.
These features ensure that HDPE pipes are low maintenance and provide a cost-effective and reliable infrastructure solution.
Why HDPE Is Resistant to UV Radiation
I searched for the top three sites to understand how HDPE resists UV radiation. These sources state that the main reasons for the HDPE’s resistance to UV radiation are its inherent properties and the inclusion of specific stabilizers. For starters, HDPE is a polymer with a permanent carbon backbone with some baseline UV resistance. However, to strengthen this, it is customary for industries to add UV stabilizers such as carbon black, which absorbs and dissipates UV radiation, thereby preventing the deterioration of the polymer chains.
Technical parameters that substantiate HDPE’s UV resistance are:
- Carbon Black Content: To protect the High-Density Polyethylene from ultraviolet light, conventional HDPE materials are compounded with 2-3% carbon black to provide adequate UV protection, absorbing and neutralizing UV radiation.
- Molecular Structure: Oxidative degradation may be reduced because the long chain structure of HDPE allows it to hold its shape when exposed to sunlight.
Such technical factors, in total, enable the HDPE pipes to be useful for outdoor applications while maintaining their pleasure and effectiveness for a long time, even with direct exposure to sunlight.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long Service Life
During the analysis of the first three websites, I came across certain factors, which, according to my manufacturing knowledge and professional experience, are responsible for the cost-effectiveness and the long service life of the HDPE Pipes. First, due to the high density of polyethylene, these pipes possess a unique characteristic: the resistance to the broadest range of corrosion, chemical, and environmental stress. Even more than that, the pipes are replaced or repaired less often; therefore, the maintenance costs are lowered significantly over time. Secondly, because of its low density, HDPE lightens the pipes, making them easier to transport and reducing the effort needed to install them.
The appropriate technical parameters that warrant these benefits include:
- Material Density and Toughness: Owing to the molecular density of HDPE, this material is rugged and highly impact resistant, which makes it long-lasting and does not suffer from breakage so easily.
- Flexibility: HDPE pipes’ flexibility limits issues associated with ground movement or earthquakes, enhancing their service life.
- Joint Integrity: Due to fused joints, HDPE Pipes are more resistant to leaks and infiltration; therefore, they are ideal and efficient solutions for many applications.
These aspects make the HDPE pipes highly sought after whenever the construction industry is mentioned as cost-efficient and durable infrastructure as per the observation of the principal online sites.
Common Plastic Pipe Types: HDPE vs. Others

HDPE pipes have different characteristics from PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and PEX (cross-linked polyethylene). HDPE is well known for its strong resistance and flexibility, which makes it suited for severe conditions and where ground movement may be experienced. Thanks to its rigidity and cost-effectiveness, PVC is very popular in drainage and plumbing applications. However, it falls short in flexibility when compared to HDPE. PEX has good thermal insulation and is widely used in home water systems, but its environmental resistance, especially UV and chemical resistance, cannot compete with those of HDPE. Ultimately, these materials will have more or less the same properties, but the decision will depend on the application. However, pricing, environmental factors, and the installation process will be crucial in selecting one.
Comparing Polyethylene Pipe to PVC and Metal Pipes
Polyethylene pipes, particularly HDPE, have a few advantages over PVC and metal pipes, according to the findings from most plumbing articles. For instance, unlike PVC pipes, HDPE pipes are flexible and can bend to accommodate dynamic areas where ground movement or vibrations may occur. In conjunction with heat-fused joints, this flexibility results in a leak mechanically secured system, thereby protecting against water losses and the chances of roots getting through.
On the other hand, while inexpensive and rigid, PVC pipes do not feature the resilience against harsh environmental conditions that is characteristic of HDPE. Such pipes are adequately capable of performing in constant pressure applications in stable soil environments but may get damaged if angular force or movement is applied.
Compared with metal pipes, pipes manufactured from HDPE have the most superior character in the picture of corrosion or chemical attack as metal pipes rust over a period and require maintenance. In addition, ease of handling and installation is achieved through lightweight HDPE, which significantly lowers labor costs.
Such properties of materials/structures as temperature, much proven over the industry standards, include:
- Flexural Modulus: HDPE usually shows lower flexural modulus, allowing for better flexibility in HDPE versus the rigid form of PVC.
- Tensile Strength: High tensile strength is undoubtedly the forte of metal pipes. However, current technologies wherein high-density polyethylene use can endure relatively high pressure adequate for most water transportation.
- Density and Weight: Compared to metal and PVC, HDPE has a smaller density, which results in lower weight, making it cheaper to transport and easier to install.
- Thermal Conductivity: HDPE reduces heat loss in systems due to having better temperature insulation than metal.
Naturally, the decision depends on the nature of the particular project, its environmental conditions, and budget limitations, but often, HDPE is the preferred and dependable solution.
Advantages of Flexible Plastic Pipe Used in Various Industries
Various sectors utilize flexible plastic pipes like HDPE because of their properties and characteristics falling within standard parameters. Such pipes are popular in construction, agriculture, oil and gas industries.
- Corrosion and chemical resistance: Flexible plastic pipes resist corrosion and chemical attacks more than metals. This enables these piping systems to convey different fluids, including corrosive chemicals, without any risk of failure.
- Cost-effective and durable: These pipes are long-lasting and require minimal maintenance; hence, they are cost-effective. They lower repair and replacement intervals, which are essential in large applications such as water and wastewater containment and distribution.
- Light and easy to bend: Flexible plastic piping systems, being light, enable easier installation and transport of the piping systems and hence reduce manpower requirements and associated costs. Their flexibility is advantageous when movements or earthquakes occur, as rigid materials tend to break.
Justification of Technical Parameters:
- Flexural strength: This ensures that during operation, the external load, internal pressure, and stresses due to structural components do not crack the pipe.
- Impact strength: This gives the construction a robust quality in cases where it is used in an area where mechanical stress or physical impact is expected.
- Thermal Stability: This appropriate performance is retained under a wide temperature range, which is important in oil and gas industries where temperature changes are experienced.
- UV Resistance: This makes it possible to perform outdoor installations without any degradation from sunlight, regarding time as a factor.
In the end, flexible plastic pipes act as a multipurpose solution that meets high industrial standards and ecological requirements, emphasizing their application for contemporary constructions.
HDPE as a Durable Pipe Solution
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes have been reported as one of the most reliable options because of their excellent durability and economic advantages. Based on significant sources, these pipes provide a unique combination of physical and chemical properties with a wide range of applications.
- Durability and Longevity: The pipes made using HDPE are impact and abrasion, allowing them to be used longer in demanding circumstances. This remarkable property helps in reducing the frequency of replacements and proves cost-effective as well.
- Chemical Resistance: These pipes resist several chemicals, which is advantageous in sectors where such aggressive substances are to be dealt with. They do not corrode and maintain physical structure without metallic counterparts, which ensures chemical stability.
- Flexibility and Ease of Installation: The HDPE pipes have a certain degree of flexibility, which makes their installation easier as they can accommodate movements of the ground originating from seismic activity or heavy loads. Not only does this feature reduce the time taken for installation, but it also reduces costs related to labor.
Models Validation:
- Flexural Strength: The HDPE pipes have high flexural strength, allowing them to sustain the mechanical stresses in such demanding conditions.
- Impact Resistance: Their enhanced impact resistance offers protection during handling and during use to prevent damage.
- Thermal Stability: These pipes are very useful over a broad temperature range for hot and cold water distribution systems.
- UV Resistance: HDPE has excellent self-resistance against UV degradation, which allows the materials to be exposed outdoors for long periods.
In summary, HDPE pipes are a feasible and long-lasting alternative for many infrastructure services as they meet industrial requirements and environmental issues, as discussed on many leading websites.
Specialized HDPE Pipe Systems

When looking into specific applications of HDPE pipe systems, it is essential to bear in mind the versatility and innovations pointed out by the leading sources. Hi, as this internet article said, polymer pipes made of HDPE systems are said to be best for water supply networks as they can eliminate leaks and not allow bacteria to grow. In the case of landfill drainage systems, the best option can be HDPE pipes due to their chemical resistance and flexibility, which greatly enhance their performance in seismic areas. Also, they serve an essential purpose in the mining field, where they withstand the high-pressure usage required to transport slurry and tailings. Undoubtedly, the American-style composite of pipes will work for most industries because of their characteristics, such as flexibility, strength, and minimal care for them.
Leak-Free Pipe and Fittings
Concerning dealing with the seamlessness of the pipes and fittings based on the majority of the sites analyzed, the following fundamental aspects and technical parameters are formulated:
- Fusion Technology: The leading sources show that for the case of HDPE systems, the two main techniques used to create a leak-proof seal are butt fusion and electrofusion, effectively creating a joint with minimal risk of leak. These fusion methods lead to the joint being the system’s most vital feature as the weakest link strengthens.
- Pressure Ratings and Specifications: It is, therefore, critical that these pipes and fittings are classified according to pressure ratings, such as SDR11 or SDR17, amongst others. Such specifications guarantee that the pipe will not fail under set pressure conditions, thus aiding the hose system in remaining leak-proof.
- Material Quality and Standards: One way of enhancing these quality characteristics is to use high-density polyethylene material of good quality that meets set standards and specifications, such as ASTM D3350, to exhibit good stress cracking and other environmental effects. Such quality is fundamental to the scope of leak integrity.
- Proper Installation Techniques: Some credible ecosystems suggest the best practice for installing HDPE systems is to carefully follow the detailed installation instructions, which include trenching and bedding.
Experts from such websites point out that the combination of these two strategies, along with exact technical parameters, enhances the waterproof performance of HDPE systems in the water supply system cumulatively.
HDPE for Wastewater and Sewage Applications
The first step in considering HDPE for wastewater and sewage purposes is to find information regarding its suitability and effectiveness, as reported by reputable sources. The leading websites list out a few benefits and technical aspects that further explain the rationale behind its adoption:
- Chemical Resistance: HDPE material exhibits excellent resistance to chemical and corrosive elements in wastewater and sewage. Such durability is critical to ensure that the material will not deteriorate from the constant aggressiveness of chemicals around it, which would lead to leakages over time.
- Flexibility and Toughness: The earth’s surface comprises various landscaping features. Therefore, the material’s flexibility is beneficial for installation in multiple terrains. It is also important to note the toughness of the material in tension or impact, which is vital due to the non-uniform nature of underground conditions.
- Joint Integrity: As in other cases, confusion in the joint is to be prevented by applying fusion technology. The fusion process embeds wires in readiness for the pole-to-pole joint fusion process, eliminating the joint position as the weakest structural member within a ductile iron pipe and making the system accessible from leak points.
- Size and Flow Capacity: For sewage and other wastewater systems, size requirements define the flow capacity of HDPE pipes; accordingly, specific sizes can be selected. The proper choice of size guarantees that the flow rates are maintained at the required levels, which lowers the chances of overwhelming the system or blockage.
These factors emphasize why HDPE is desirable in wastewater and sewage treatment: streamed materials research and industry-related online resources back them.
Innovative Pipeline Solutions Using HDPE
While thinking of new pipeline solutions using HDPE, several critical considerations must be considered for achieving the desired results, as documented by the most reputable sources. First of all, studies emphasize the material’s long-term strength and environmental resistance, with studies proving that HDPE can withstand several stresses while effectively performing. Second, lifecycle analyses, which demonstrate decreasing upkeep and substitution expenditures over the years, emphasize HDPE’s affordability. Such understanding and rationale can be found on sites such as Engineering Insider, Plastics Technology, and the Plastics Pipe Institute.
In addition, the specific technical characteristics which are essential for HDPE pipelines are as follows:
- Temperature Resistance: HDPE has a broad operational temperature range, making it suitable for other regions with varying climatic conditions.
- Thermal Expansion: The low coefficients of thermal expansion and contraction minimize potential movements in the system.
- Pressure Handling: The ability of the material to withstand different pressure ranges assures reliability in varying operational environments.
Justifiable in current industry practices, such parameters also portray HDPE as a stout material suitable for constructing global pipeline networks, advocating its use in modern-day construction.
Reference Sources
- Plastics Pipe Institute (PPI) – The Plastics Pipe Institute provides comprehensive resources and technical guidance on using HDPE pipes in various applications. Their documentation and case studies highlight the advantages and diverse uses of polyethylene solutions, making it a valuable source for understanding the feasibility of HDPE in industrial applications. Visit Plastics Pipe Institute
- American Water Works Association (AWWA) – AWWA offers a wealth of information regarding water supply systems, including using HDPE pipes. Their publications and standards are widely recognized for providing insights into the effectiveness and reliability of HDPE in ensuring leak-proof and durable water systems. Explore American Water Works Association Standards
- ScienceDirect – This scientific database hosts numerous articles and research papers that examine the properties and applications of HDPE pipes across different sectors, including environmental engineering and industrial processes. The peer-reviewed papers available on this platform can validate the practicality and benefits of HDPE in various industrial scenarios. Access Research on ScienceDirect
- American Water Works Association (AWWA) – AWWA offers a wealth of information regarding water supply systems, including using HDPE pipes. Their publications and standards are widely recognized for providing insights into the effectiveness and reliability of HDPE in ensuring leak-proof and durable water systems. Explore American Water Works Association Standards
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

What is HDPE, and why is it commonly used for pipelines?
HDPE, or High-Density Polyethylene, is a type of plastic known for its high strength-to-density ratio, longevity, and resistance to various environmental factors. These properties make it an ideal material for pipelines, particularly in applications that require durability and leak resistance.
How does HDPE compare to other materials in terms of cost and sustainability?
While the initial cost of HDPE pipes can be higher than some alternatives, their long-term durability and minimal maintenance requirements often result in cost savings over time. Additionally, HDPE is recyclable, contributing to its sustainability compared to other pipeline materials.
Are HDPE pipes suitable for hot water applications?
HDPE pipes are generally used for cold to moderately warm water applications. Other types of pipes, such as those made from cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), are more suitable for hot water due to their better temperature resistance.
What types of joints are used in HDPE pipeline systems?
HDPE pipeline systems often use heat fusion joints, including butt welding and electrofusion, to create secure and leak-proof connections. These methods are preferred because they make a homogenous joint that maintains the integrity of the pipe material.
Can HDPE pipes be used to supply potable water?
Yes, HDPE pipes are approved for use in potable water supply systems and are known for their non-toxic properties and resistance to biofouling, ensuring safe and clean water delivery.





