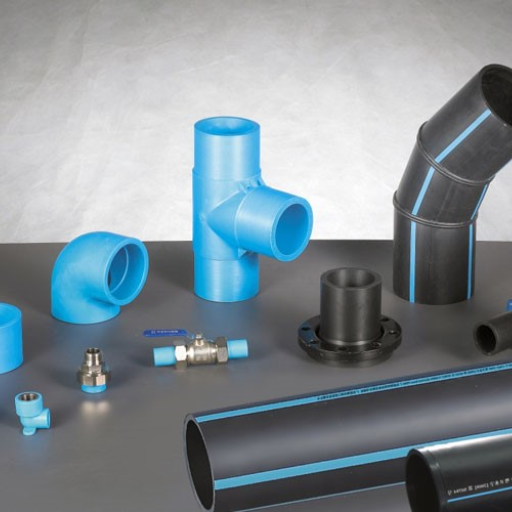
In a wide range of sectors, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Pipes have become crucial components in addressing multi-faceted applicational needs; their responsiveness to temperature, pressure, and corrosion has enabled the smooth engineering of modern-day pipes for civil engineering and environmental protection. Most people know that modern-day High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are durable, flexible, and highly resistant to corrosion. In this article, we specifically look at the most common types of HDPE pipes, their specific characteristics as well as their specific applications. This guide will be beneficial to a creation worker, environmental engineer, or anyone who wants to know more about eco-friendly material alternatives. In order to achieve project targets both in the short and long term, it is critical to evaluate the opportunities available in the market.
What are the different types of HDPE pipes that are available?
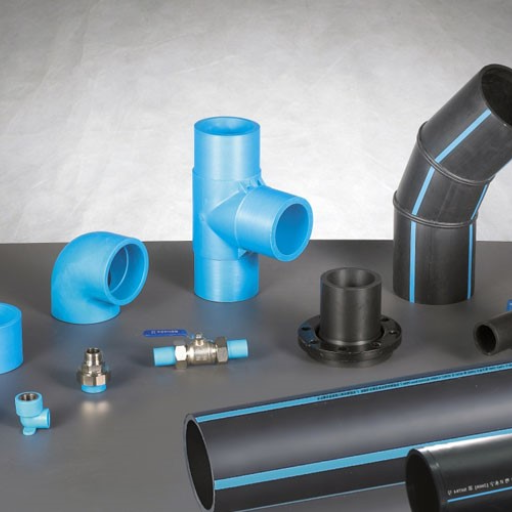

HDPE pipes come in several types, each tailored for specific applications and conditions. The most common types include:
- Single-Wall Corrugated HDPE Pipes: As a result of their lightweight and flexibility, which facilitate easier fitting in different types of terrains, these products are commonly applied for drainage solutions.
- Double-Wall Corrugated HDPE Pipes:Intended for more advanced usage, these pipes come along with strength and durability which make them suitable for piling systems as well as for sewage and stormwater management systems.
- Chemical-Resistant HDPE Pipes: Designed to withstand low-aggressive chemicals and high-temperature conditions, these pipes are best suited for industrial applications that require the transportation of such extreme substances.
- High-Density HDPE Pipes: Given their strength and the ability to cope with high pressure, these pipes find application in water transmission and distribution systems.
The particular characteristics of HDPE pipes allow users of this construction material to select solutions that best satisfy their projects’ requirements since the benefits of the HDPE material are retained.
Various Types of HDPE Pipes
In the various fields of HDPE piping systems, several types of pipes exist with distinct purposes and uses. The various types consist of:
- Solid Wall HDPE Pipes: They are the most popular and find applications in the distribution of water, irrigation, and sewage. An Advantage of their design is that they are highly resistant to pressure.
- Corrugated HDPE Pipes: These pipes are indeed lightweight, flexible and, owing to their configuration, are able to perform adequately under external loads. As a result, they are most often employed in drainage systems and culverts.
- HDPE Duct Pipes: Typically used in telecommunication and electricity works, these evaporate materials are used mainly due to their simple application and flexibility in use.
- Perforated HDPE Pipes: These types of pipes are specifically optimized for sub-drainage systems. The perforations enable water to flow freely through the pipe which makes them well suited for farm and landscape draining.
There’s an engineering aspect behind each type of HDPE pipe which allows it to withstand environmental constraints as well as specific technical requirements. This has enabled customization in various industries.
Overview of HDPE Pipe Types
As a skilled professional in the field, it is important to note that there are different classifications of HDPE pipes, each intended to be used for designated purposes. The most common types include:
- Corrugated HDPE Pipes: Perfect for drainage systems as well as for sewer applications because of their elasticity and strength.
- Smooth Wall HDPE Pipes: These are mainly employed in the safeguarding of electrical wires and telecommunications because of their sturdy and non-corrugated shape.
- Ductile Iron Size (DIPS) HDPE Pipes: Structured to fit into the ductile iron pipe sizes, making them ideal for in-place reinforcements of the existing iron pipes in the utility networks.
- Iron Pipe Size (IPS) HDPE Pipes: Applicable for various purposes in the field of water distribution and able to accommodate standard iron pipe sizes.
- Coiled HDPE Pipes: Typically deployed in rural gaseous and irrigation distribution systems, their flexibility and coiling allow long runs without joints.
Each of these types has distinct characteristics that are suitable for differing industrial needs guaranteeing the best performance in certain fittings. Familiarity with these distinctions is helpful in choosing an HDPE pipe for a particular application.
HDPE Pipe Manufacturing Process
The evolving manufacturing process of HDPE pipes consists of several stages that aim at accomplishing the targets of quality and durability of the pipe. First, raw material in the form of HDPE resin pellets is charged into the extruder, where these resin pellets are melted and homogenized. The molten HDPE is then passed through a circular die where the length of the pipe is formed by the extrusion process. Immediately after the formation of the die, the molten pipe is cooled and hardened in a vacuum-calibrating chamber in order to keep the dimensions and wall thickness within the tolerances. Afterward, the pipe is allowed through a sizing section for further dimensional corrections if needed. Lastly, the pipe goes through a water splash, where it is further cooled off and cut to size as required. From the beginning all the way to the end, control measures are put in place, for example, temperature, pressure, and extrusion velocity monitoring, and at regular intervals, visual and dimensional checks are done to ensure that the pipe is compliant with the required regulation.
How Pipes Come in Various Sizes and Dimensions
The size or dimension of HDPE pipes is proportionate to the intended use, the requirements of the project in question, or the measures set by industry standards. The pipes are manufactured in a number of diameters, which are expressed in mm or inches, and cater to various flow rates and pressure ratings. The wall thickness of the pipes also differs, depending on pressure ratings such as SDR or Standard Dimension Ratio, which is the thickness of the wall in comparison to the diameter of the pipe. This permits flexibility to be tailored for certain requirements on water supply, gas lines, sewage systems, and industrial ones. It is possible to modify extrusion conditions and tooling such that the required pipes for any installation can be achieved and assured for proper usage and durability.
How Does the Design of HDPE Pipes Impact Their Usage?

I’m here to tell you how the design of HDPE pipes determines their usage in the simplest words possible. It is important to note that HDPE pipes are designed bearing in mind a number of key parameters that directly affect their workmanship and applications.
- Material Composition: High-Density Polyethylene is the raw material used to produce the HDPE Pipes. This material is strong, flexible, inert to chemicals, and excels in resistance to stress cracks. Such a composition guarantees that they can survive harsh conditions and endure for an extended period of time.
- Diameter and Wall Thickness: The diameter and wall thickness are critical areas since they fix the rating of pipe pressure and the capacity of flow. Different projects have different specifications. Therefore, pipes can be made to meet the required performance.
- Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR): The diameter-to-wall thickness ratio of the pipe is defined by the solid wall ratio or SDR. The optimal SDR change results in rule performance depending on the strength or pressure required.
- Flexibility: Pipes produced from HDPE are flexible by nature and hence it permits easy installation which is useful in areas that are unlevelled or where no trenching techniques are used. This flexibility also minimizes the impact of ground movement on the pipes decreasing the probability of a leak.
- Jointing Techniques: Pipes of HDPE are joined through welding joints, be it a butt fusion or an electro-fusion joint; these joints are completely leak-tight. This is a critical feature for avoiding loss of water and ensuring the overall system integrity in the case of pressurized lines.
Taking into account these parameters while designing the HDPE pipes, they can be manufactured to suit certain categories. This would provide efficiency, reliability, and life cycle of the application in question whether for water supply or for gas distribution.
Understanding the Design of HDPE Pipes
The design of these parameters will guarantee that, when creating the HDPE pipes, they may be made in accordance with certain categories. This would ensure the longevity of the efficiency and reliability of the application whether it is for the distribution of water or gas.
- Material Composition: The main constituent of HDPE pipes is high-density polyethylene which is quite durable and has the ability to resist chemical attacks. Their strength to overcome environmental stresses makes them suitable for prolonged usage in various geoclimatic conditions.
- Diameter and Wall Thickness: The pressure rating and flow capacity of HDPE pipes depend on the diameter and wall thickness of the pipes. Thus, pipes can be perfectly adapted to meet the needs of the project, in accordance with the requirements outlined.
- Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR): In pipe design, SDR is critical as it relates to the ratio of a pipe’s diameter to its wall thickness. By varying SDR, performance can be targeted, influencing the ability of the pipe to be subjected to various pressures and loads.
- Flexibility: HDPE pipes provide ease of installation especially when using the trenchless installation technique or installing them on uneven grounds due to their inherent flexibility. This characteristic also assists in mitigating potential damage from ground movement thereby increasing the life of the pipe.
- Jointing Techniques: To make sure that their functionality and structural integrity are preserved in cases involving high-pressure applications, it is crucial to ensure that the joints are HDEPE pipes tightly fused using advanced fusion jointing techniques, butt or electromuffusion, which in turn leads to joints that are both leak-proof and strong.
The design parameters definitely ensure the HDPE pipes work properly for the intended purpose for instance, simple, yes, to design HDPE pipes for water supply systems. They have a multipurpose approach towards the pipes and provide the pipes requirements needed for such functions rather than focusing on water supply requirements only.
Mechanical Properties of HDPE Pipe
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are distinguished by their exceptional mechanical properties. Most importantly, this implies that these pipes have high impact strength, and therefore, they remain intact under duress and mechanical stresses. Their tensile strength offers longevity and the ability to survive immense internal and external forces. HDPE pipes also have good fatigue resistance, and as such, they are suitable for use in conditions with cyclic loads. All together, these attributes make HDPE ideal for use in many harsh environments, with dependable and durable solutions for stiff and flexible systems.
How Diameter Affects Performance
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are distinguished by their exceptional mechanical properties. Most importantly, this implies that these pipes have high impact strength, and therefore, they remain intact under duress and mechanical stresses. Their tensile strength offers longevity and the ability to survive immense internal and external forces. HDPE pipes also have good fatigue resistance, and as such, they are suitable for use in conditions with cyclic loads. All together, these attributes make HDPE ideal for use in many harsh environments, with dependable and durable solutions for stiff and flexible systems.
What are the Advantages of HDPE Pipes?

In my professional opinion as an industry expert, I would agree that HDPE pipes have several prospects that make them suitable for use in several pipe applications. Some of these benefits are given below:
- Flexibility and Durability: HDPE pipelines are sufficiently bent at the required angle during installation, especially in complex geography, because they are very flexible. This flexibility also reduces the chances of joints failing and allows them to last for a long time.
- Corrosion Resistance: HDPE pipes possess distinct advantages over metal pipes by showcasing a durable characteristic that is corrosion proof. This implies that they are fit for the transportation of water, chemicals, and even fluids which would have led to deterioration of metals.
- Low Weight: HDPE pipes weigh less, which makes both transportation and installation easier. That lowers total labor and installation expenses.
- Longevity: Due to their life expectancy of 50 to 100 years, HDPE pipes are extremely dependable in terms of durability since they lower the number of times one is required to substitute and replace them consistently.
- Leak-Free Joints: Fusion welding of HDPE pipes ensures a solid union without any leakage. As a consequence, this technology is superior than mechanical joints which tend to leak with time.
- Environmental Friendliness:HDPE pipes do not pose a threat to the environment because they come with the guarantee of being completely recyclable and their attributes will not be affected upon being reused.
- Impact Resistance: HDPE pipes have an outstanding ability to withstand severe conditions such as freezing and high impacts without rupturing or splitting, therefore possessing a great impact toughness.
In light of these considerations, the benefits of using HDPE pipes become evident, making them a preferred option to be used for a much wider variety of piping systems.
Benefits of Flexible Plastic Pipe
Having worked on such projects in the past, I would like to highlight some benefits brought forth by the enhancement of technology when dealing with flexible plastic pipes, most importantly HDPE pipes. Their inherent flexibility allows them to be used in a wide range of unfriendly environments, ensuring easy installation and minimal joint failures in the future. As I have seen, HDPE pipes allow for the selection of noncorroding materials, which ultimately provides high reliability for the system over time. In addition to this, the low density of HDPE polymer allows for easier transportation and handling during installation, lowering our costs and expenses significantly. The operating duration of the pipes can be as high as 100 years allowing for fewer replacements and changes in the system in regards to maintenance. The heat fusion technology used in their manufacture allows for conducive joints without the possibility of leakage, which is important for the integrity of the system. Also, the fact that they are environmentally friendly does not harm the environment or the ecosystem and is tough further enhances their value. All these attributes are more than enough to prove why incorporating flexible plastic pipes such as HDPE into our systems is simply the best option.
Why Pipes Are Also Resistant to Corrosion
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are very resistant to corrosion thanks to the fact that they are made of high-density polyethylene, which is generally passive to many chemicals. Accordingly, this material will not oxidize and corrode like metal pipes. Hence, it does not suffer the same decay when stressed with moisture, strong chemicals, or extreme weather conditions. It’s the nature of HDPE at the molecular level to create a shield against the entry of oxygen, which is a cause of corrosion. Thus, this resistance not only increases the life of the pipe but also enhances the efficacy and effectiveness of the systems where these pipes are installed and reduces expensive repairs and maintenance.
Compared to Traditional Pipes
During my analysis of HDPE pipes as compared to normal metal or concrete ones, it became crystal clear the advantages of HDPE. Through my experience, normal pipes, although, in the past, have been reliable, have had to make more elevations in the maintenance aspect as most have corrosion and joint leak issues. Such problems could cause increased operational downtimes and maintenance costs. However, this is not the case with HDPE pipes, as they provide uninterrupted work due to the problems that metal pipes commonly have, which are all disappearing. They also flex well enough to withstand ground movements without cracking, which is a great asset when taking into consideration the sort of ever-changing environments we tend to install into. Also, the HDPE’s light weight reduces the logistical burden and saves on both time and labor. All things considered, an investment-able system in terms of HDPE materials not only improves the structure of the system but also encourages a clever investment approach that pays attention to the ideas of efficiency, economies of scale, and sustainability.
How to Effectively Join HDPE Pipes?
The proper joining of the HDPE pipes is very crucial as this ensures a consistent and leak free network. There are several methods for joining HDPE pipes, suitable for various applications and specific project requirements. Below is a list of common methods, along with details on each:
- Butt Fusion
Pero, Butt fusion es uno de los métodos más habituales que se utilizan para unir tuberías de polietileno hdpe. Este mecanismo implica el calentado de las dos extremidades de un tuberia las cuales son posteriormente unidas, siendo esto un proceso irreversible. Les resulta adecuado para tuberías de gran diámetro. Para esta tarea, con el fin de asegurar un correcto posicionamiento y calentamiento, también se requiere de instrumentos específicos. Las investigaciones han mostrado que los empalmes a tope pueden igualar o superar la resistencia uniaxial de la propia tubería, lo que otorga una alta durabilidad.
- Electrofusion
The peculiar method of electrofusion is practically used across industries that offer electrofusion services. Cutting the surface of pipes to create a domestic fit is required, thus making two welding ends melt each other. The molten ends effortlessly joined together, even those that struggle to attach in an electrofusion machine. It is, therefore, recommended that electrofusion machines be used together with fusion welding. This allows for the welding of multilayered fiber-reinforced plastics, conducting pipes, and different functions of pipes. The method fosters the attachment of a large variety of fittings and has been reported to possess superior joint reliability ability. Meaning this method is highly advantageous for places that are interfered with using butt welds when such fittings are required.
- Socket Fusion
Socket fusion Welding is mostly used for smaller unionized thermoplastics, Such as Polyethylene (up to 4 inches diameter); this method greatly resembles butt welding except one end of one of the pipes is inserted into a heated socket so that the pipe end melts and fuses with a fitted socket. This makes it a stronger joint and requires less equipment, thus reducing the cost of smaller projects. Achieving a successful joint using socket fusion greatly depends on the correct technique.
- Mechanical Fittings
As long as circumstances surrounding either prefabrication or the installation itself do not allow for thermal fusion, mechanical fittings may serve as beneficial options. Typically, these fittings are clamped or pressed on the pipe providing a form of mechanical coupling. Even though they are usually more costly than welding, easier and faster connection is achieved, and the use of special tools is not required. They have the benefit in situations of repair where systems are to be restored fast. If done perfectly, these methods also maintain the quality and function of the systems of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes, tailoring them to suit the project’s requirements while reducing the chances of leakage and failure risks.
Techniques for Joining HDPE Pipes
In the works of HDPE pipe fittings, the choice of a method depends on the specific requirements of the project and its surroundings. Butt fusion is considered an economic basis for strong permanent joints, which are best suitable for big pipelines where space permits. However, when dealing with small diameters, sock fusion reliably does the job, albeit it requires careful methods to achieve proper junctions. Mechanical fittings are, however, more expensive but are quite useful when quick repairs are required or when thermal fusion is difficult or impossible to do. In any case, all the mentioned methods have their purpose, and in this way, all of them provide a wide range of functional and reliable features for various types of HDPE applications.
Understanding Butt Welding Method
In my opinion and experience, the butt welding method of HDPE pipe joining is very successful in big projects. What this method requires is the heating of both ends of two pipe sections, placing them together, and allowing them to cool so that they join together. Obviously, to achieve a strong joint that does not leak, it is essential that the pipe ends being joined together are absolutely in line with each other. The equipment used for welding and the operator’s expertise are determining factors of the success achieved. There are many instances where I have used butt welding to joints and fittings in instances where long lengths of pipe installations had to be done and when the necessary equipment was available in the project site. When it comes to butt welding, each time, I pay close attention to the parameters – temperature, pressure, and alignment because if I don’t, it will not produce the best possible joints in HDPE piping.
The Role of Fittings for HDPE
In the capacity of an industry expert, I can elucidate the specifics of the butt welding method and the important factors in a clear manner. Using this technique requires taking several factors into account in order to achieve a sound and leak-free joint. Here they are, one by one:
- Temperature: For the connection of HDPE pipes to be done efficiently, the ends of the pipes need to be exposed to heat at an appropriate temperature which usually falls between the range of 400 degrees Fahrenheit and 450 degrees Fahrenheit or 204 degrees Celsius and 232 degrees Celsius. In order to bring about uniform heating, it is important to use a relevant heating plate with a uniform across its surface temperature.
- Pressure: Perfect application of pressure facilitates proper bonding of the joins, as too much pressure will result in distortion of the pipe ends, and too little would lead to a weak joint. The recommendations from the manufacturer regarding the specific pipe diameter must be adhered to.
- Alignment: Prior to pressing, it is critical that the ends of the piping systems be in perfect position. If this alignment fails, there is potential for gaps, discontinuities, or weak regions to form within the joint. This procedure can be executed in a more controlled manner by using fixtures or clamps which help in the positioning.
- Cooling Time: Neglecting to provide a sufficient period for the joint to cool when still under pressure is something not to be taken lightly. As the joint cools down measurably, the material set, hence transforming the weld. Attempting to hurry through this phase may result in failure of the joint.
- Equipment Calibration: Regular checks and calibrations of welding equipment are necessary to maintain the accuracy of set temperatures and pressures for the desired output.
It is possible to securely and robustly join HDPE pipes by butt welding if these factors are strictly controlled.
What are the Disadvantages of HDPE Pipes to Consider?

As I researched HDPE pipes, I also came across a few disadvantages that I think need to be kept in mind as well. To begin with, it is clear that HDPE pipes can endure damage and cannot be exposed openly to UV radiation, which means that such pipes with UV exposure would require added protection. Secondly, it shall be noted that HDPE pipes have a higher tensile strength than other materials, which results in an ability to withstand higher amounts of temperature and pressure before succumbing. This specific characteristic as well requires the need of good design in order to allow thermal expansion and contraction in running systems, this is particularly pertinent in projects that measure long lengths of pipe.
Furthermore, though HDPE pipes have a fair bit of advantages when it comes to their integration into structures, this can compromise their flexural strength, making it difficult to maintain their bonding and structure in some fixtures. I have also had an experience in which I found out that installing HDPE pipes wasn’t very convenient because their flexibility made the process more complex. Also, butt welding, for instance, may be hard to put smaller components together when skilled workers do not have the requisite equipment or experience to ensure correct pair welding techniques. While these weaknesses don’t necessarily outdo the numerous benefits of HDPE pipes, they are important considerations that I need to keep in mind while analyzing the usefulness of this type of pipe in each specific case.
Potential Drawbacks of High-Density Polyethylene Pipe
As an industry expert, I comprehend the issues involved in this subject matter, and I will do my best to explain them in a straightforward manner. The potential disadvantages can be categorized as follows:
- UV Radiation Susceptibility: Pipes made of HDPE are prone to degradation due to the micromolecules within them being broken down by the sun’s UV rays. However, such exposure usually does not affect a pipe’s performance significantly if the pipe is simply coated or buried underground. These steps preserve the strength and functionality of the pipes in outdoor settings.
- Thermal Expansion: Pipes produced from High-density polyethylene have a relatively high thermal expansion which allows them to expand and contract more that is the characteristics of the material. In view of this the writer recommends planning for both expansion and contraction during design and installation. One can mitigate these repercussions through expansion loops or expansion joints.
- Flexibility Challenges: Taking into account that HDPE pipes are flexible can lead to certain stresses and movements while at the same time, pose challenges in maintaining shape and alignment. Misalignment can be remedied through failed planning and installation strategies such as appropriate anchoring and support.
- Joinery Expertise: The weld joints involved in the construction of butt-welded HDPE pipes may sound simple enough. However, they do require an element of skilled workers and precision tools for their assembly. For smaller projects, alternate joining methods such as electrofusion, which can be easier to handle, can be considered.
Neverthless, it is necessary to understand and respond to these limitations strategically in order to fully integrate the benefits accruing from use of HDPE pipes in the relevant applications.
Challenges in Pipeline Installation
The very first step in solving the complications existing with the installation of pipelines is to comprehend the properties of the material and the influences of the natural environment on the specific process, as an industry expert would see it. First of all, to minimize the effect of UV radiation, ringing protective coatings onto an HDPE pipe and/or using soffit placement to avoid prolonged lateral exposure to the sun is recommended. Secondly, the effects of thermal expansion should be designed into the structure through precise design, where expansion joints are located in regions where the change in longitudinal length induced by temperature should be catered for.. In order to allow the flexibility of the pipes, strong anchoring systems are required to control the alignment and stability of the pipes. Moreover, it is also important to have a good knowledge of the various methods of joinery; hiring well-trained workers and buying good equipment is a good investment because this way, the integrity and durability of the pipe joints will be increased and consequently improve the quality of installation and the service.
Expert Perspective on Environmental Conditions Susceptibility
On the basis of my work experience, it is worth noting that there are environmental vulnerabilities associated with the use of HDPE pipes. There is apprehension regarding UV damages, but this can be contained by using various coatings and locating the systems in shaded or buried positions. Whenever working on projects, I actively consider thermal expansion issues and address them by placing expansion joints and accounting for the temperature within the design. Also, the use of appropriate anchoring techniques ensures that the pipeline does not shift position due to the effects of the environment while allowing reasonable degrees of movement if necessary. My advanced skills and the application of some specific internal and external splitting joinery techniques that I possess enable me to see to it that every pipe installation not only complies with the professional requirements but withstands adverse environmental conditions which in turn guarantees the durability and reliability of the HDPE pipeline systems under my charge.
Where Can You Use HDPE Pipes?
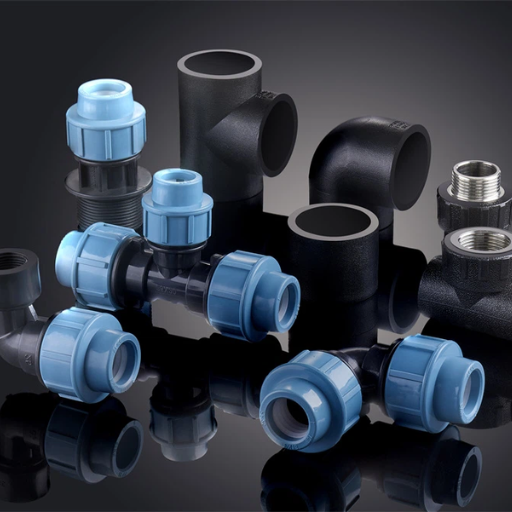

HDPE pipes are multi-purpose and can be applied across many sectors. They are ideal for water supply systems, as well as wastewater, owing to their excellent strength and anti-corrosive properties. In agriculture, HDPE pipes are suitable for irrigation purposes since they help transport water over long distances in an efficient manner. They are also used in industries for the conveyance of chemicals and gases on account of their resistance to chemicals. Moreover, in telecommunication, HDPE pipes are used as protective tubes for underground cables, thus protecting them.
Common Use of HDPE Pipes in Industries
The industrial application of HDPE pipes may be explained by their strength and flexibility. In the case of water and sewage, they are an excellent choice since they are non-rust and durable. Sectors such as agriculture utilize HDPE pipes for irrigation in an economical way to reduce the use of water. In many cases, HDPE pipes are used in the industry to transport chemicals because they can withstand corrosion. Moreover, HDPE is also used in telecommunications to protect cables. These applications have proven the variety and efficiency of HDPE pipes across many industries.
Why HDPE Pipes Are Used in Water Supply
Due to their exceptional endurance and flexibility, HDPE pipes have been found to be useful in water supply systems. As a result of their resistance to corrosion and chemical interactions, these pipes can be sustained over time in comparison with conventional materials, thus saving on maintenance and cutting down on downtime. The characteristic smooth interior of HDPE reduces surface friction, which helps improve flow and reduces pumping energy used to transport water. Also, the adaptability of the thermoplastic HDPE pipes to extreme locations and weathering factors makes them suitable for different geographical regions. These combined features explain their increasing adoption and preference in modern water supply systems.
Applications in Gas Pipe Systems
Due to their safety and reliability, HDPE pipes are extensively used in gas pipe systems. Their flexibility enables straightforward installation on uneven surfaces, and their lightweight construction eliminates challenges in handling, thus lowering the cost and length of installation. The high resistance of HDPE to stress cracking entails a long service life, making it a suitable option for high-pressure gas lines. Furthermore, the butt welding of the HDPE pipes produces a leakproof joint, thereby improving the integrity and safety of the system. Such features explain why HDPE pipes are a popular material in modern gas distribution systems.
Reference
- HDPE – Plastic Pipe Institute: Provides insights into HDPE pipes used in building and construction, particularly for geothermal applications.
- HDPE Pipes Features And Applications: Discusses the various applications of HDPE pipes, including water supply, gas distribution, and sewage systems.
- Learn about HDPE Piping – WL Plastics: Provides information on the safety, reliability, and maintenance of HDPE piping systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types and designs of HDPE pipes that are available?
A: HDPE pipes come in various types and designs, including high density polyethylene pipe, HDPE 80, and HDPE 100. These pipes are classified based on their diameter, wall thickness, and rated working pressure. They are extruded through a die to create a range of HDPE pipes that can be used for fluid and gas transfer.
Q: What should I know about HDPE pipes?
A: HDPE pipes are known for their flexibility and durability. They are widely used in various applications, including water supply, sewage, and industrial pipelines. HDPE pipes also have a high resistance to chemicals and environmental stress, making them suitable for a wide range of conditions.
Q: What are the benefits of using HDPE pipes?
A: HDPE pipes offer numerous benefits, such as being lightweight yet strong, having excellent corrosion resistance, and being flexible. This flexibility allows the pipes to absorb stress from external forces, reducing the risk of damage. Additionally, HDPE pipe fittings allow for easy connections and modifications.
Q: How is the pipe wall thickness of HDPE pipes determined?
A: The pipe wall thickness of HDPE pipes is determined by a combination of factors, including the pipe’s intended application, the working pressure it needs to withstand, and the material’s properties. The speed of the screw during the extrusion process also plays a role in determining the wall thickness.
Q: What are the common HDPE pipe joining methods?
A: The most common methods for joining HDPE pipes include butt fusion and electrofusion welding. These methods ensure a strong and leak-proof connection. HDPE pipe fittings are joined using these techniques to maintain the integrity of the pipeline.
Q: What is the role of carbon black in HDPE pipes?
A: Carbon black is used in HDPE pipes to enhance their UV resistance. It helps prevent degradation from sunlight exposure, which is crucial for pipes installed above ground. Black HDPE pipes are usually preferred for outdoor applications due to this added protection.
Q: How do I select the appropriate HDPE pipe diameter for my application?
A: The selection of HDPE pipe diameter is determined by the flow rate, pressure requirements, and the type of fluid or gas being transported. Pipe outer diameter, rated working pressure of HDPE, and the specific needs of the project must all be considered to ensure optimal performance.
Q: Can HDPE pipes be used for slurry applications?
A: Yes, HDPE pipes can be used for slurry applications. Their flexibility and resistance to abrasion make them suitable for handling slurries. However, selecting the correct pipe wall thickness and diameter is essential to manage the pressure and flow characteristics of the slurry.
Q: Are there specific HDPE pipes for different industries?
A: Yes, HDPE pipes are designed to meet the needs of various industries including water supply, sewage, mining, and industrial applications. The types of pipes and pipe fittings used are often determined by the specific requirements of each industry.
Q: How does pipe length affect the installation of HDPE pipes?
A: Pipe lengths can affect the ease and cost of installation. Longer pipe sections reduce the number of joints needed, which can lead to quicker installations and fewer potential leak points. However, handling and transportation of longer pipes may require special equipment and considerations.






